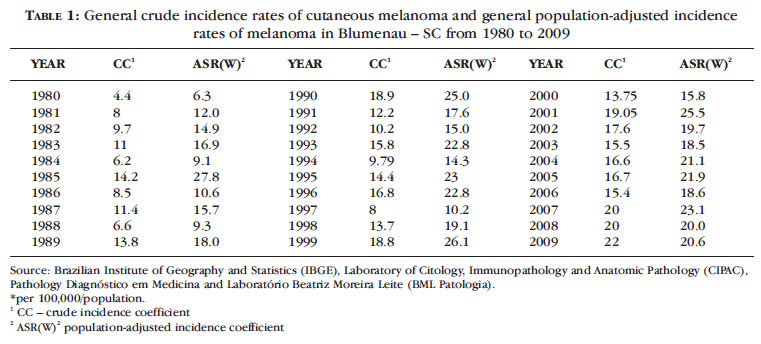
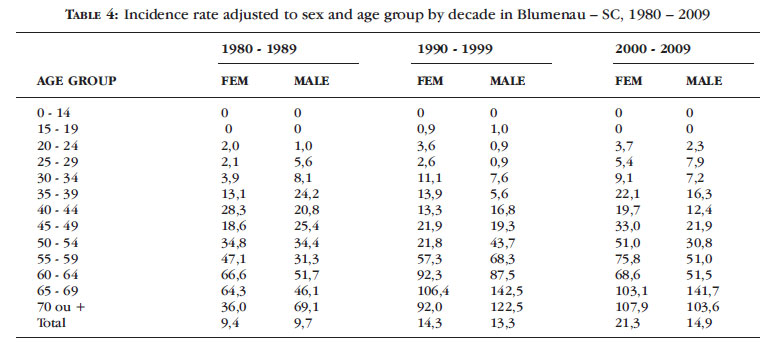
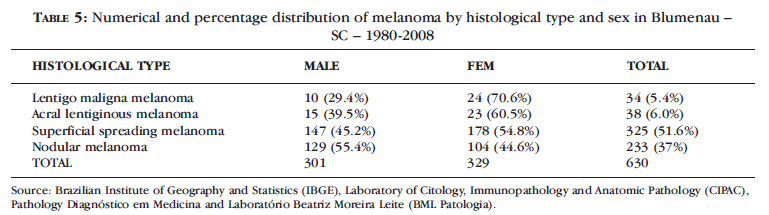
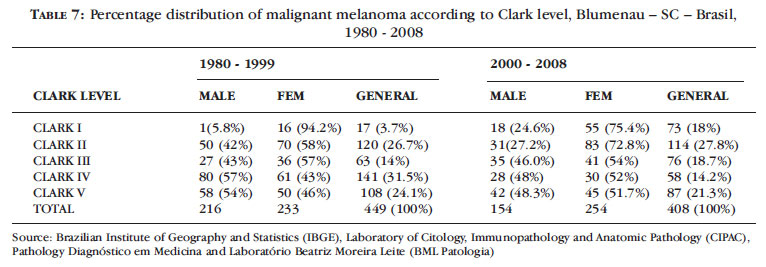
BACKGROUND: Melanoma incidence and mortality rates have increased over the past 30 years in the Caucasian population. In Brazil, data on non-capital cities are scarce, making epidemiological stu dies necessary. OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the incidence of and classify cutaneous melanomas in Blumenau from 1980 to 2009. METHOD: Data from 1002 histopathological examinations of individuals from Blumenau were collected, considering sex, age, primary site of involvement, histological type, level of invasion (Clark's level) and tumor thickness (Breslow's depth). The gross and adjusted coefficients of annual incidences were calculated based on the number of melanoma cases and the population estimated by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) between 1980 and 2009. RESULTS: The incidence rates of melanoma reached 22.4 cases per 100,000 inhabitants/year; 31.5 in women and 30.4 in men at the adjusted rate. The incidence rates standardized by decade, age and sex were 141 male and 103 female cases per 100,000/inhabitants aged 65 to 69 years. Superficial spreading melanoma occurred in 53% of the cases, followed by nodular melanoma (37%), and the primary site of involvement was the trunk (47%). 62.5% of the cases were diagnosed early, with Breslow < 1mm. CONCLUSION: The incidence of malignant melanoma has increased fivefold from 1980 to 2009 and early diagnosis has increased 151% as a result of primary prevention
Early detection of cancer; Early diagnosis; Epidemiology; Melanoma; Morbidity