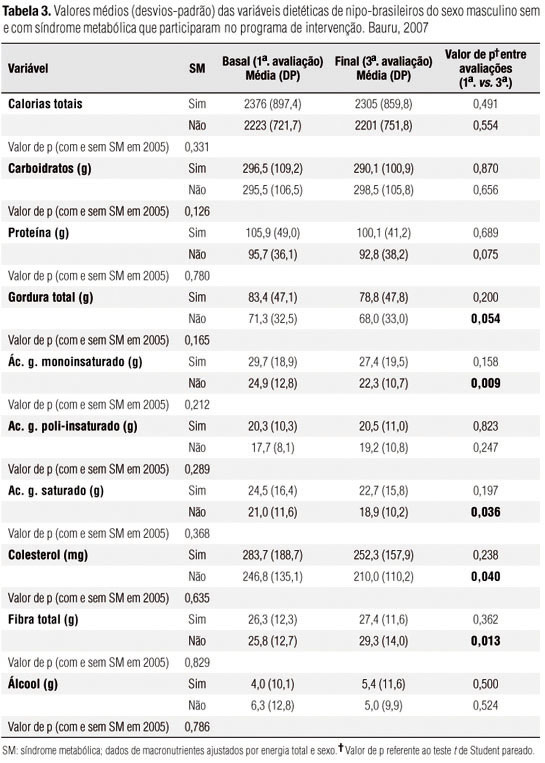
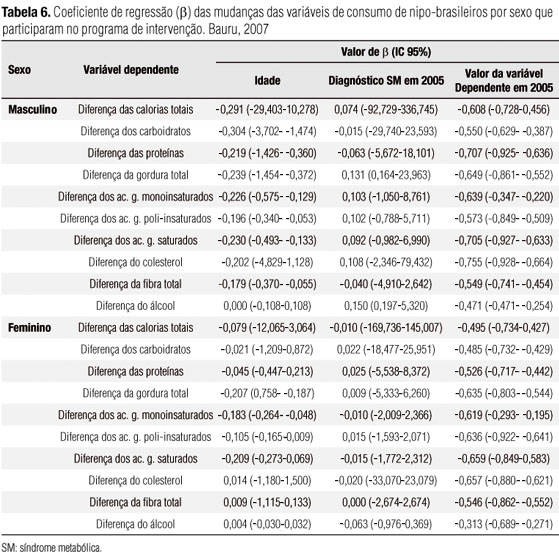
OBJECTIVE: We evaluated the changes in biochemical and nutritional profiles of Japanese-Brazilians with and without metabolic syndrome after two years of participation in the intervention program. MATERIALS AND METHODS: It was a non-controlled experimental study. The biochemical and clinical assessments were conducted at baseline (2005), after a year (2006) and after two years (2007) of intervention. On the present study, data of 360 individuals, who participated on the three assessments were considered. RESULTS: Both groups presented improvements on the anthropometric and metabolic profile, after two years of intervention. It was observed reduction in the intake of total fat, saturated fat, and dietary cholesterol, and increased intake of fiber among men without metabolic syndrome. It was observed reduction in the intake of total fat (p = 0,003) and monounsaturated fatty acid (p = 0,002). CONCLUSION: The results showed a positive impact of the lifestyle intervention program in metabolic and nutritional profile of Japanese-Brazilians with and without metabolic syndrome.
Nutritional epidemiology; nutrition intervention; metabolic syndrome; Japanese-Brazilian; nutrition; chronic diseases