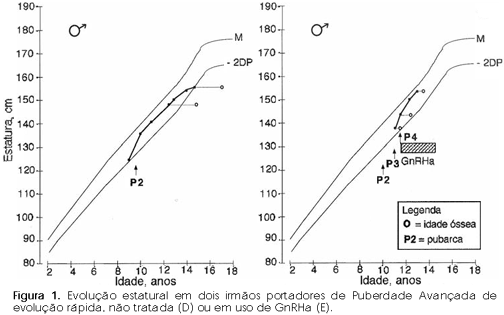
Pubertal development is associated with increased growth velocity secondary to the interaction of three hormones: sex steroids, growth hormone and IGF-1. The pubertal spurt represents 16% of adult height. Precocious puberty (PP) may induce early fusion of growth plates, reducing growth duration and, consequently, adult height. Thus, the main objective of the treatment with GnRH analogues is to avoid the height commitment. It is important to emphasize that PP does not evolve uniformly, sometimes having a slow course (slow evolutive form), which does not require treatment. The authors discuss aspects of normal pubertal growth, precocious puberty and its variants, and the effects of treatment on final height. Special situations as early and fast puberty are also mentioned.
Precocious puberty; Early puberty; Fast puberty; Growth; GnRH analogues