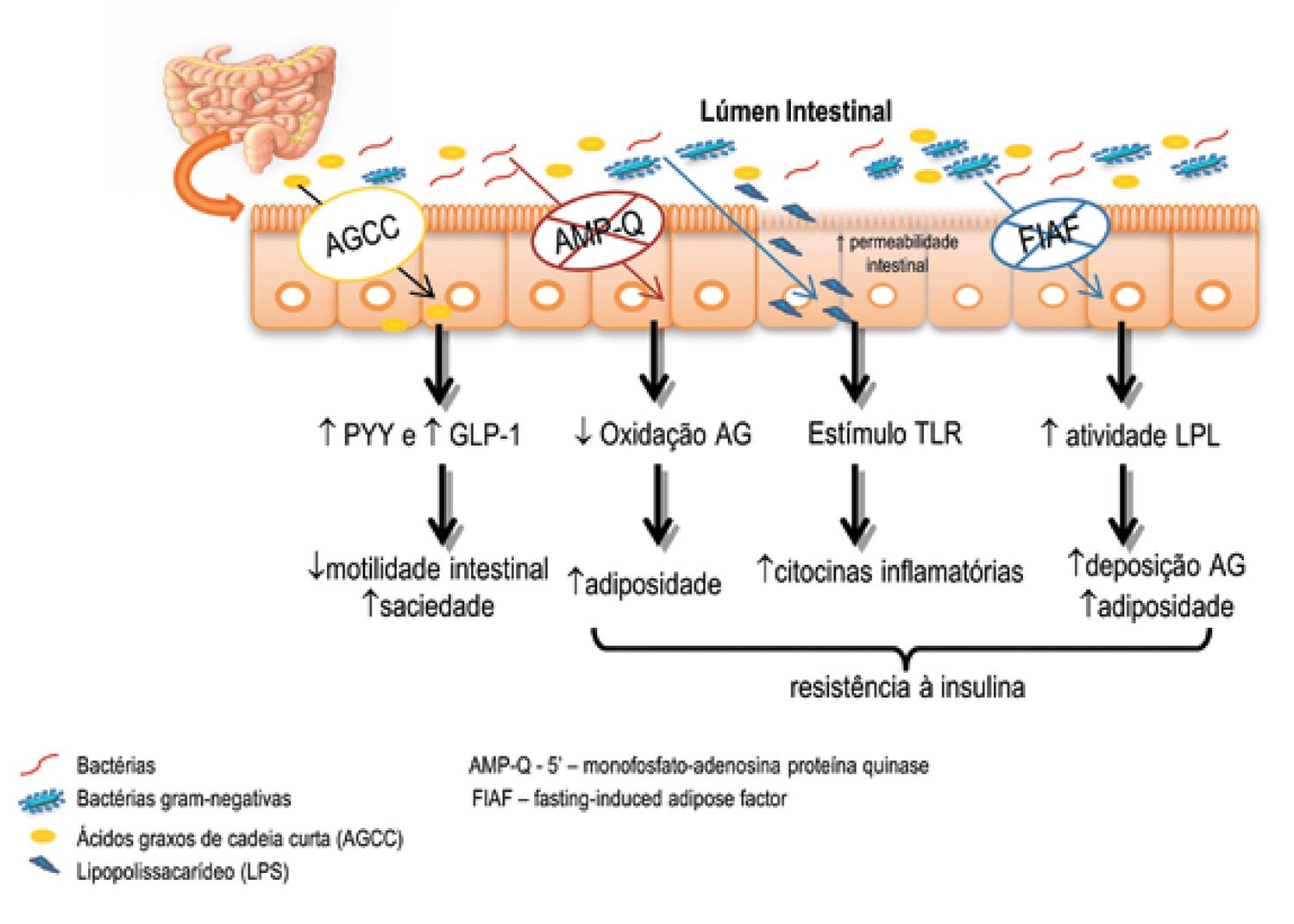
The gut microbiota obtained after birth is composed of a large range of bacteria that play different roles in the human host, such as nutrient uptake, protection against pathogens and immune modulation. The intestinal bacterial content is not completely known, but it is influenced by internal, and mainly by external factors, which modulate its composition and function. Studies indicate that the gut microbiota differs in lean and obese individuals, and in individuals with different food habits. There is evidence that the relationship between diet, inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiometabolic risk are, in part, mediated by the composition of intestinal bacteria. Knowledge about the gut microbiota may result in different strategies to manipulate bacterial populations and promote health. This review discusses the relevance of understanding the role of dietary factors or patterns in the composition of the microbiota, as well as pathophysiological mechanisms of chronic metabolic diseases, and the potential of prebiotics and probiotics on the cardiometabolic risk profile.
Gut microbiota; food habits; inflammation; insulin resistance; body adiposity