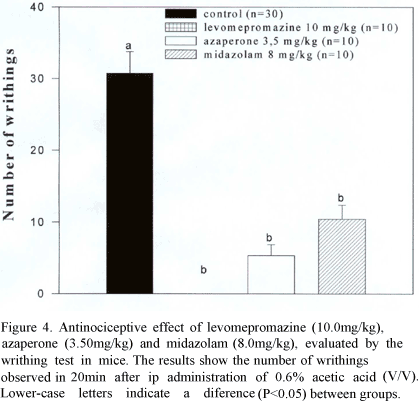
The sedative and antinociceptive effects of levomepromazine, azaperone and midazolam were studied in rats and mice using three behavior evaluation methods. Both exploratory behavior and spontaneous locomotor activity were significantly diminished in a spontaneous locomotor activity test in open field when using levomepromazine and azaperone. However, the azaperone effects were short lived in comparison to levomepromazine effects. Midazolam caused reduction in exploratory activity with no effect in spontaneous locomotion. When assessing the antinociceptive effect in the tail flick reflex latency test after infliction of a pain stimulus in rats, tested drugs did not show any antinociceptive effect. The drugs studied were able to abolish the writhing reflex in mice when compared to control. Levomepromazine, azaperone and midazolam, at the doses were able to inhibit the exploratory behavior in rats, proving their sedative effect. Regarding the antinociceptive effects for visceral pain, these drugs were able to block contortions in mice.
sedation; nociception; levomepromazine; azaperone; midazolam