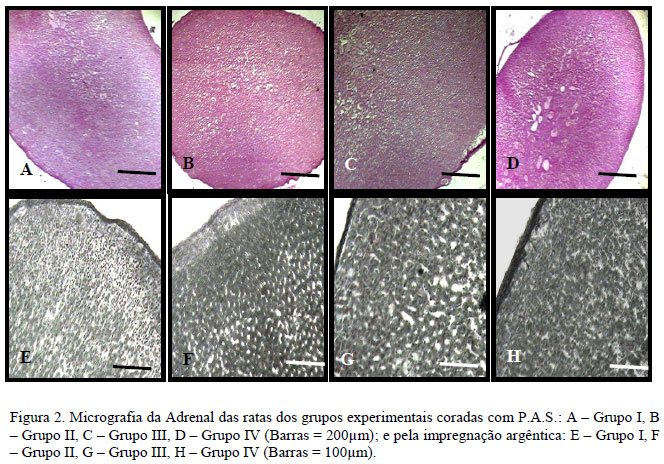
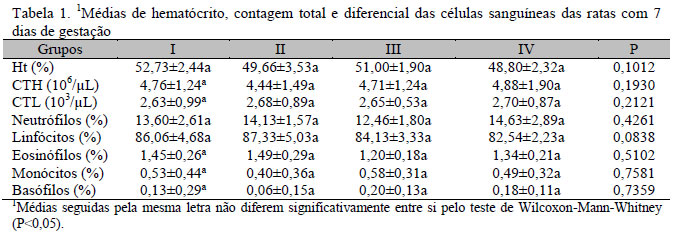
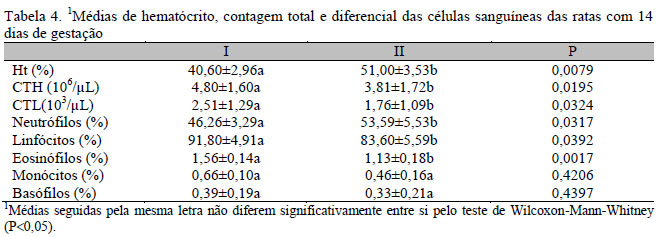
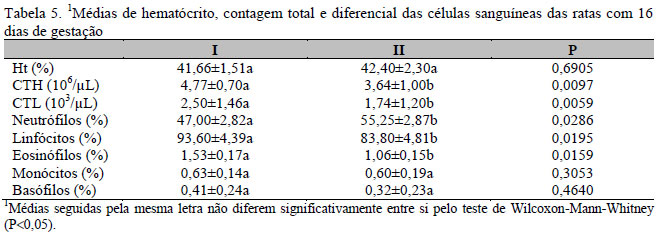
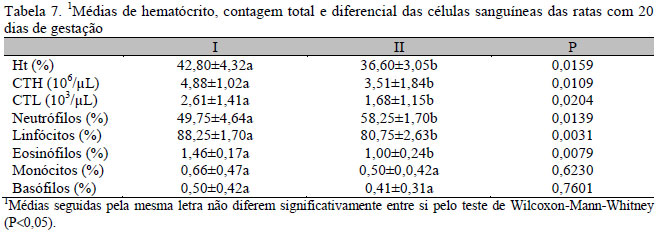
Dexamethasone is used in cases of pregnancy with prematurity risk. However, it may affect the embryogenesis when used in supraphysiological doses. Melatonin has been shown to prevent the deleterious effects of glucocorticoids. Therefore, the influence of melatonin on the effects of dexamethasone on pregnant rats was evaluated through the following parameters: 1. Hemogram and glucose profile; 2. Progesterone levels; 3. Histomorphometry and histochemistry analyses. Twenty female rats were divided into the following groups: I - rats that received placebo (Control); II - rats treated with dexamethasone (0.8mg/kg); III - rats treated with melatonin (0.5mg/kg); IV - rats treated with dexamethasone and melatonin. All treatments started 10 days after confirmation of mating and lasted until the end of the pregnancy. Blood samples were collected on the 7th, 14th, and 21st day. Carbohydrate and progesterone levels were determined with the antrona and ELISA method, respectively. The liver, kidneys, and adrenal glands were analyzed morphometrically and histochemically. On the 7th day of pregnancy there were no significant changes in the parameters analyzed. However, at 14 days of pregnancy there was a significant increase of hematocrit, reducing the total number of erythrocytes and leukocytes, neutrophilia, lymphopenia, eosinopenia and reduced diameter of red blood cells in rats treated with dexamethasone. These effects remained on the 21st of day of pregnancy, except for the hematocrit, which was reduced. There was also a significant reduction in glucose levels (21st day) and progesterone (14th and 21st days). There was no change in the histochemical and morphometric parameters in the liver, kidneys and adrenals. Dexamethasone at a dosage of 0.8mg/kg administered from the middle third of pregnancy produces hematological, biochemical and hormonal changes in rats, being prevented by melatonin, but does not affect the liver, kidneys and adrenal glands regarding morphometric and histochemical parameters.
rats; melatonin; glucocorticoid; hemogram; pregnancy