Abstract
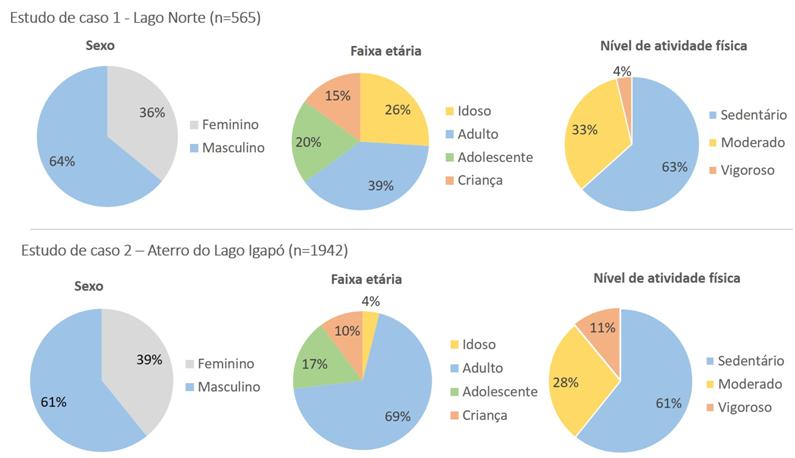
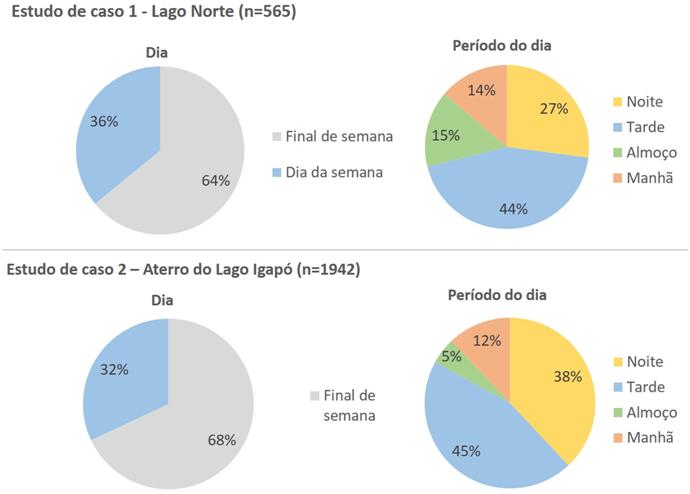
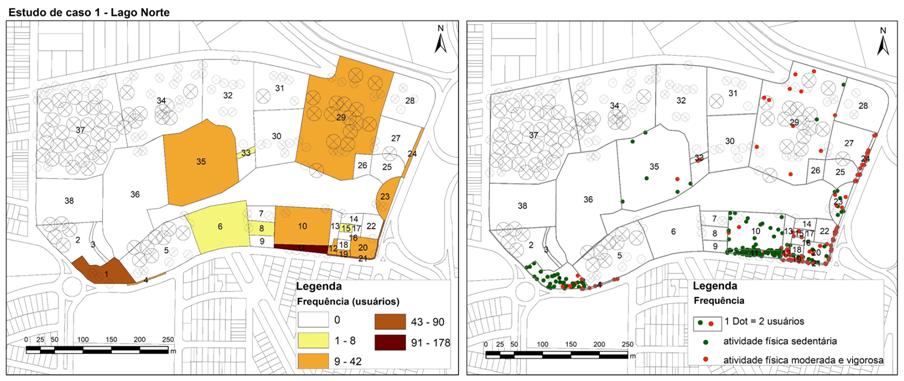
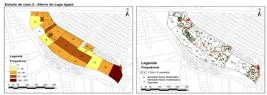
Many studies have been highlighting theimportant role of public spaces in supporting a healthier life. The aim of this research was to verify the existence of an association between the spatial configuration of parks located in different socioeconomic areas and physical activity. The methodological strategy used was a comparative case study in two urban parks in the city of Londrina, Paraná, Brazil. Two protocols were adopted, SOPARC (System for Observing Play and Recreation in Communities) and PARA (Physical Activity Resource Assessment), to collect data from users, activities, intensity of physical activity and the parks’ characteristics. The results indicate there is an association between facilities such as open-air gyms, hiking trails, sports fields, picnic areas and bleachersand the practice of moderate/vigorous physical activity. The analysis showed qualitative differences in terms of insertion, access, immediate surroundings and the parks’ different conditions. The results contribute to the establishment ofspatial guidelines in park designs, as well as topromote an interdisciplinary debate on the use of protocols validated and applied in the Health field.
Keywords:
Built environment; Public open space; Physical activity; SOPARC; PARA

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail

 Fonte: adaptada de
Fonte: adaptada de  Fonte: adaptada de
Fonte: adaptada de