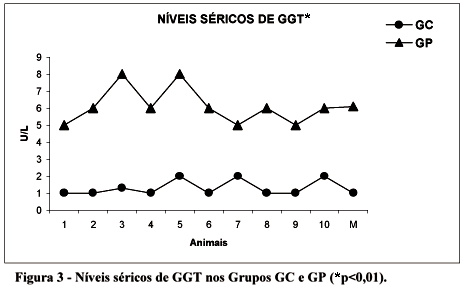
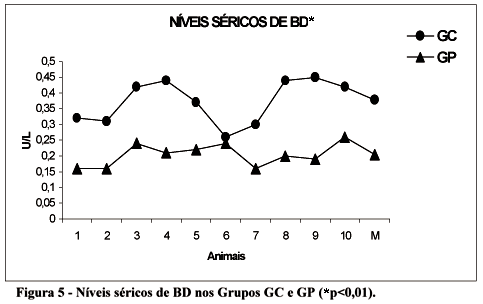
Copaiba oil is a oil-resin used as a phytotherapic in Amazon region in a folkloric way. This use is empirical and little is known about its effect in the organic systems. Objective: To determine serum levels of aminotransferases, bilirrubins and gama-glutamyl transpeptidase after copaiba oil administration. Methods: Male Wistar rats (n=20) divided in two groups of 10 animals: Group Cop which received a daily oral administration of copaiba oil, 0.63ml/kg, during 5 days; Group P in which any substance was administrated. In the sixth day the animals of both groups were submitted to inalatory anesthesia, laparotomy and collection of blood samples (3ml) from inferior vena cava for the determination of serum aminotransferases, bilirrubins and gama-glutamyl transpeptidase levels. Results: The results were compared between groups and analyzed by t-Student test. Group Cop showed AST, ALT and GGT levels significantly decreased when compared with Gruop P (p<0.01), while total bilirrubins levels increased by its direct fraction. Conclusion: Copaiba oil can alter serum levels of aminotransferases, bilirrubins and gama-glutamyl transpeptidase, showing a possible interaction between this substance and liver, but this considerations require posterior evalutaion.
Medical plants; Aminotransferases; Gama-glutamyltranspeptidase; Bilirrubins; Rats