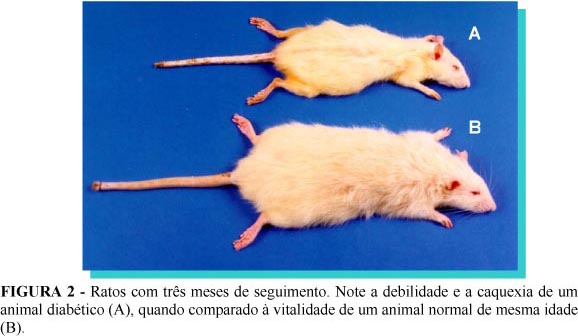
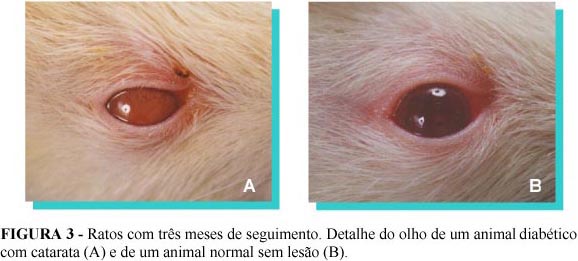
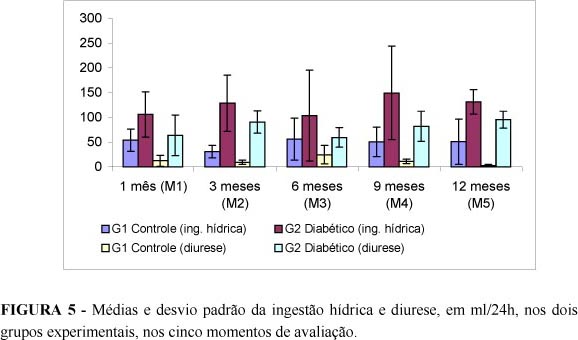
PURPOSE: This work aimed to determine the clinical and laboratory alterations of rat with Diabetes mellitus using alloxan endovenously. METHODS: The animals were randomly assigned to two experimental groups: Normal Control Group (G1) with 25 healty animals and Diabetic Group (G2) with 25 severe diabetic animals. They were evaluated in 5 moments (1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months) during which the following parameters were studied: clinical evolution (body weight, water intake, food intake, and diuresis) and biochemical exams (fast glycemia, urinary glucose, glucosuria, ketonury, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides and lipids). RESULTS: Alloxan 2% injection intravenously in the rat was followed by 39% death rate and also caused severe diabetes in 39% of the animals. Diabetes was characterized by progressive body weight loss, significative water intake, food intake and diuresis with blood glucose levels above 300 mg/dl, glucosuria 3+ and eventually ketonury. Diabetes doesn`t change profile a long-term of cholesterol and lipids levels. CONCLUSION: Our studies showed that alloxan causes clinical and laboratory alterations in the rat, what is typical of severe diabetes. They allow the long-term studies of diabetic.
Diabetes; Alloxan; Rat