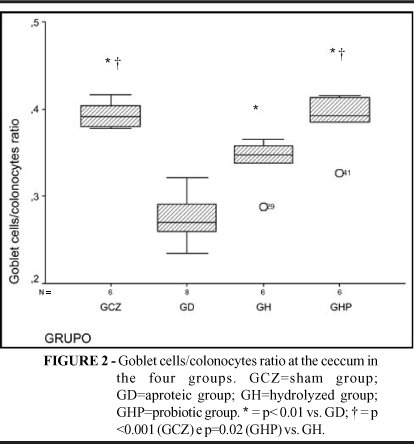
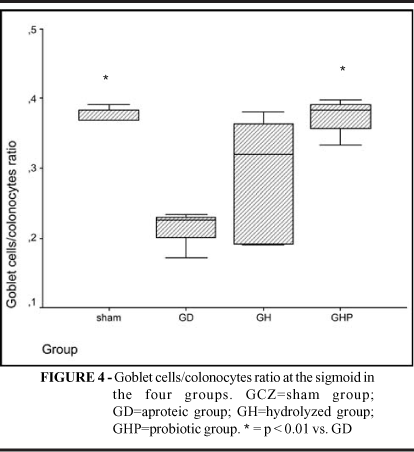
PURPOSE: To investigate the effects of the addition of probiotic bacteria to a hydrolyzed diet on the recovery of goblet cells during renutrition in an animal model of malnutrition. METHODS: Twenty-six male Wistar rats (200-250g) were included in the study. Six were kept under normal conditions (sham group) while twenty received an aproteic diet for 15 days, and were randomized thereafter to receive a hydrolyzed diet containing (n=6; probiotic group) or not (n=6; hydrolyzed group) probiotics (10(6) cfu/g of Streptococcus thermophilus e Lactobacillus helveticus); or immediately killed (n=8; aproteic group). Histological slides containing cecal and sigmoid biopsies were used to counting the number of goblet cells and the goblet cells/colonocytes ratio. RESULTS: Malnutrition diminished the population of goblet cells in all sites. Goblet cells/colonocytes ratio of the probiotic group was significantly greater than hydrolyzed group at the ceccum (0.39 ± 0.03 vs. 0.34 ± 0.02; p=0.02). Only rats fed with probiotics showed complete restoration of the normal goblet cells/colonocytes ratio at the sigmoid (0.37 ± 0,02 vs. 0.22 ± 0,03; p<0,001). CONCLUSION: Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus helveticus added to a renutrition diet enhance the recovery of mucocal atrophy induced by malnutrition and especially induce a rapid restoration of goblet cells population in the malnourished colonic mucosa.
Probiotics; Malnutrition; Goblet cell; Mucosa; Colon