Abstract
Objectives
Assess weight gain in adulthood, as well as influence on the prevalence of hypertension.
Methods
Cross-sectional study through a telephone interview with individuals ranging from 30-59 years old, section of the Municipal Monitoring System of Risk Factors for Non-Transmitted Chronical Diseases via Telephone Interview (Sistema Municipal de Monitoramento de Fatores de Risco para Doenças Crônicas Não Transmissíveis por Meio de Entrevistas Telefônicas (SIMTEL)). We analyzed demographic data, anthropometric and lifestyle. The independent effect of weight gain and current body mass index and 20 years of age in the prevalence of hypertension was analyzed using Poisson regression.
Results
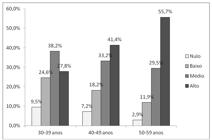
The median age was 42 years old (CI95%, 41.0-43.0). The average relative weight gain was 18.1 ± 11.1%. In the sample, 7.0% presented zero weight gain, 19.2% low, 34.2% average, and 39.4% high weight gain. In multivariate analysis, the weight gain was not associated to high blood pressure, since the current BMI was significantly associated, with a prevalence 2.4 times higher in obese than in normal weight, while in obese at 20 years of age, the prevalence hypertension was 1.9 times higher.
Conclusions
There was a high weight gain in adulthood, but this gain was not decisive for hypertension when adjusted by the current BMI.
Keywords:
hypertension; blood pressure; body mass index; weight gain; adult
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
