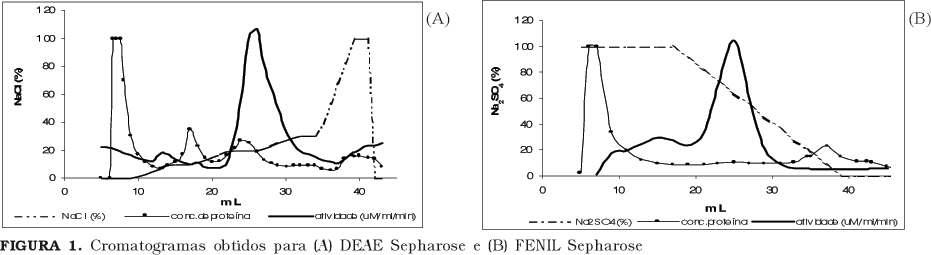
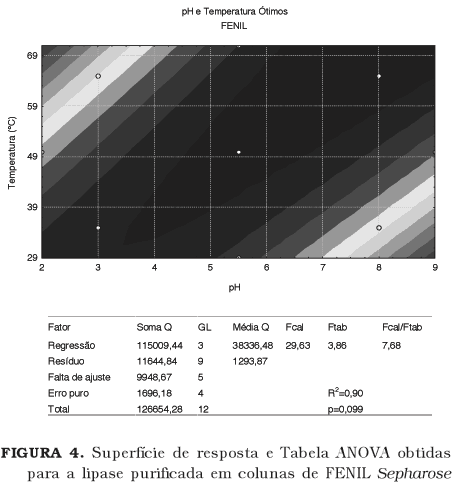
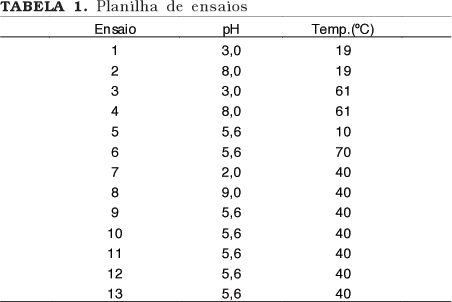
Lipases, especially of microbial origin, are widely applied in processes and in the production of insumesfor the chemical, cosmetic, pharmaceutical and food industries. To produce highly pure enzyme is important to process control (absence of interferentes). However the necessary stages to the purification, in general, cause losses of activity and increases enzyme final cost. The aim of this work was to consider the best methodology of purification for the Rhizopus sp. lipase through the test of two different chromatographic methods (ion exchange and hydrophobic interaction) and also to verify the best statistical design for the biochemical characterization of the enzyme. It was possible to partially purify the Rhizopus sp lipase applying a DEAE Sepharose (anionic exchange) column and a PHENYL Sepharose (hydrophobic interaction) column. The first, although more selective for the enzyme in study, seems to cause reduction of its activity. The presence of higher concentrations of Sodium ions in the PHENYL Sepharose fraction seems to contribute for an increased activity of the lipase. Although the results obtained through the factorial design for the biochemical characteristics of the lipase were compatible with the single variable analysis, that statistical approach should not be indicated in the present case.
ion exchange; DEAE Sepharose; hydrophobic interaction; Phenyl Sepharose; biochemical characterization