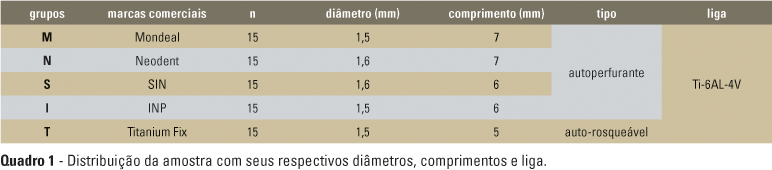
OBJECTIVE: The objective of the present study is to assess both deformation and fracture of orthodontic mini-implants of different trade marks by submitting them to loads perpendicularly applied along their lengths. METHODS: A total of 75 mini-implants were divided into five groups (n = 15) according to their manufacturers: group M (Mondeal, Tuttlingen, Germany), group N (Neodent, Curitiba, Brazil), group I (INP, São Paulo, Brazil), group S (SIN, São Paulo, Brazil), and group F (Titanium Fix, São José dos Campos, Brazil). The mini-implants were perpendicularly inserted into swine cortical bones and then submitted to mechanical tests by using a universal testing machine (Emic DL 10.000) at cross-head speed of 0.5mm/min. The force required for deforming and fracturing the mini-implants at 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0mm was assessed. Data were assessed by using variance analysis (ANOVA) and Tukey's test. RESULTS: Mini-implants of group S were found to need higher forces to be deformed and fractured in comparison with other groups whose mini-implants were submitted to lower forces, a result that is statistically significant (p < 0.05). Group M showed the lowest values regarding deformation with no statistical difference compared to group N (p > 0.05), whereas group T had the lowest values regarding fracture with statistical differences compared to groups M, S, and I. CONCLUSIONS: Based on the present study, one can conclude that the shape of the mini-implants is directly related to their flexural strength. Despite the differences reported above, the mini-implants were found to be clinically useful.
Orthodontic anchorage procedures; Mini-implant; Deformation