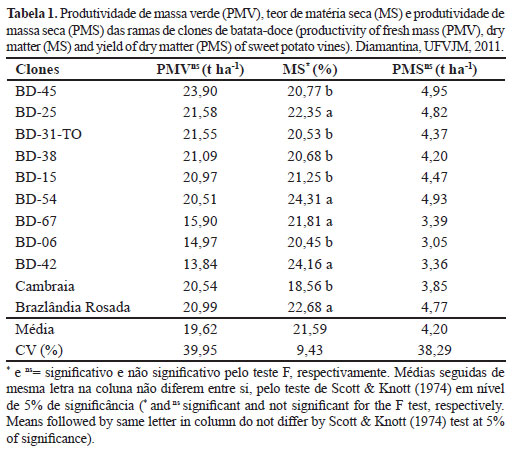
The objective of this study was to select potential clones of sweet potato for animal feeding purposes. The experiment was carried out in a randomized block design with four replications. Eleven clones BD-06, BD-25, BD-15, BD-38, Cambraia, BD-31-TO, BD-67, BD-45, BD-42, BD-54 and the cultivar Brazlândia Rosada belonging to germplasm bank of the Federal University of Vales do Jequitinhonha and Mucuri (UFVJM) were evaluated. We estimated the dry matter content and the productivity of green and dry mass of the vine. The traits pH, dry matter, crude protein phosphorus, calcium and sodium were estimated in the evaluation of silages quality. There was no significant difference in productivity of green mass and dry mass among the clones of sweet potato. The obtained silages had sufficient levels of crude protein (11.59%), neutral detergent fiber (31.98 to 39.68%), acid detergent fiber (29.65 to 35.45%) and total digestible nutrients (62.90 to 66.91%) proving the potential use of the sweet potato vine as silage in animal feeding.
Ipomoea batatas; total digestible nutrients; dry mass; neutral and acid detergent fiber; crude protein