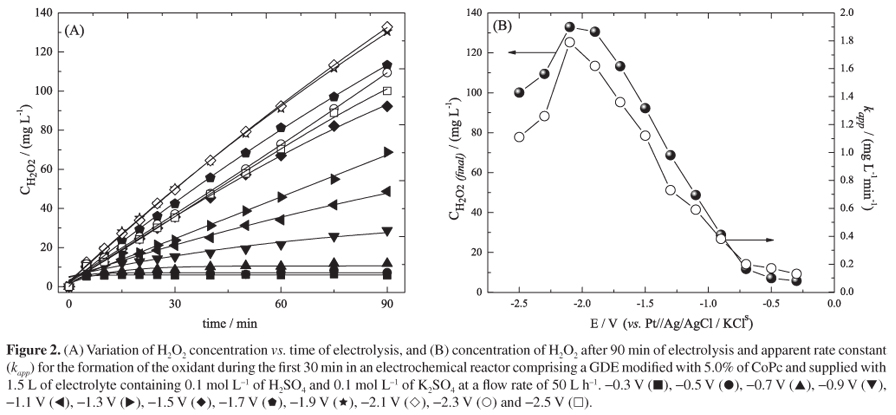
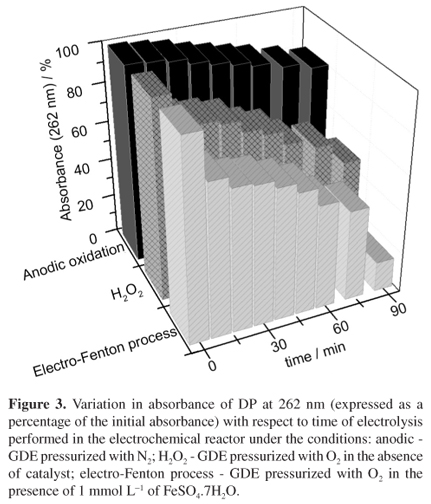
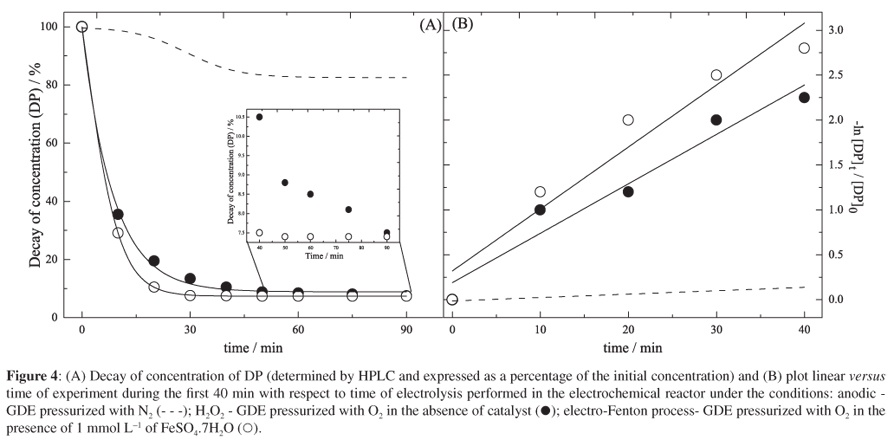
The increasing occurrence of antibiotics and their metabolites in surface and ground waters is causing a significant impact on the environment and needing of developing novel treatments for the complete removal of such contaminants. This paper presents the study of the electrogeneration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in acidic medium and the degradation of the analgesic dipyrone in an electrochemical flow reactor using a gas diffusion electrode (GDE) modified with 5.0% cobalt (II) phthalocyanine (CoPc) and pressurized with O2. The highest yield of H2O2 (133 mg L-1) was achieved after 90 min of electrolysis at an applied potential of -2.1 V (vs. Pt//Ag/AgCl/KCl s) and the best results for degradation of dipyrone were obtained under electro-Fenton conditions, where the total organic carbon (TOC) was reduced 62.8% after 90 min of reaction and 49.1 kW h of energy was consumed per kg of dipyrone degraded.
gas diffuson electrode; electrochemical reactor; dipyrone; Fenton process