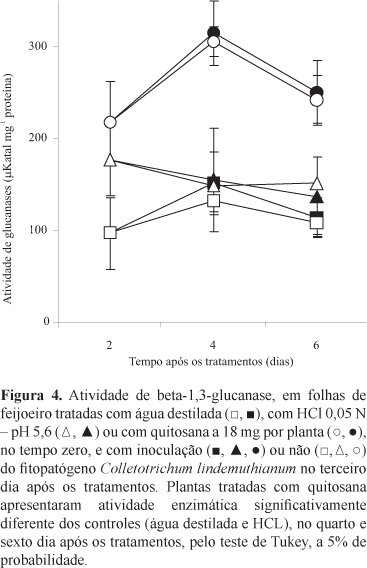
The objective of this work was to evaluate the effect of chitosan on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) anthracnose. Different concentrations of chitosan suspension were sprayed on plants at V3 stage, in greenhouse; plants were also infected with Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. The concentration of 9 mg per plant reduced the anthracnose severity in more than 50%, without causing any toxic effect on bean plants. The protecting effect was local and more intense in a time interval of 4 days between treatment and inoculation. Mycelium growth reduction and spore germination inhibition of C. lindemuthianum were observed, when chitosan was used at 1 mg mL-1 and 80 µg mL-1, respectively. Chitosan increased the glucanase activity in bean leaves. Chitosan presents antifungal properties against C. lindemuthianum, as well as potential to induce resistance on bean plants. Therefore, the plant spraying with chitosan can be an alternative to control anthracnose.
Phaseolus vulgaris; Colletotrichum lindemuthianum; antibiosis; induced resistance; pathogenesis-related proteins