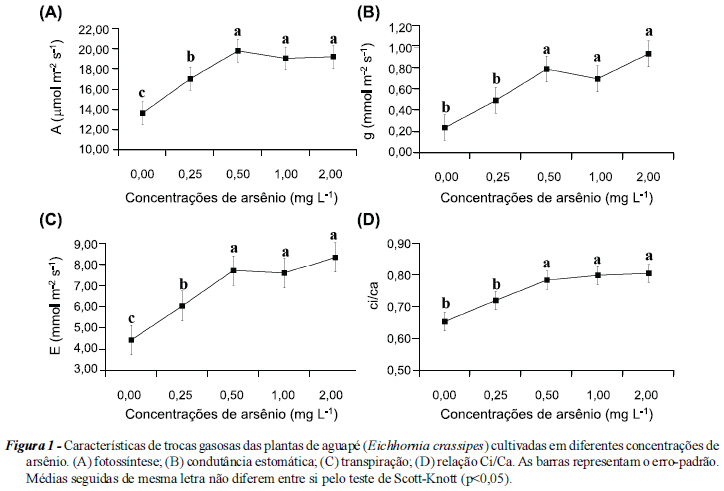
This work aimed to evaluate the anatomical and physiological characteristics of Eichhornia crassipes in response to arsenic stress. Plants of E. crassipes were grown in Hoagland hydroponic nutritive solution under greenhouse conditions at five arsenic levels: 0.0, 0.25, 0.50, 1.0 and 2.0 mg L-1 during 20 days. The plants showed an increase in photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, transpiration and Ci/Ca rate, as well as in the activity of all the enzymes in the antioxidant system, with higher activity in the leaves than in the roots, in all the treatments with arsenic. The anatomical characteristics observed on the leaves of the plants under higher arsenic levels showed an increase in stomatal density, stomatal index and spongy parenchyma thickness. Root anatomy showed no toxic evidences at any arsenic level; changes in the xylem and phloem characteristics were exhibited by the roots in the arsenic treatments, but no damage was caused to its structure and function. Thus, stress caused by arsenic intoxication at the levels tested, is not evident on E. crassipes plants, and the mechanisms of tolerance of E. crassipes are associated to anatomical and physiological changes.
Eichhornia crassipes; ecological anatomy; antioxidant system; photosynthesis