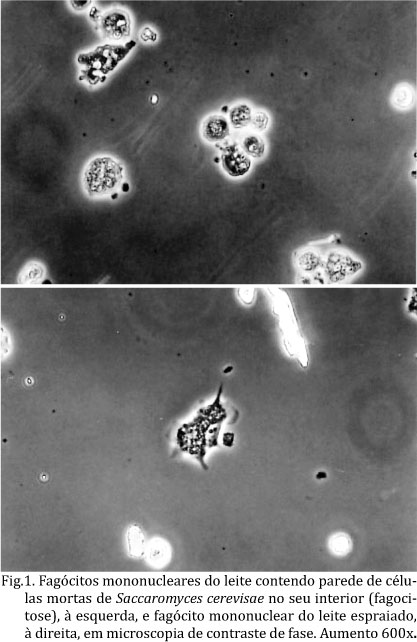
The study aimed to evaluate the cell viability, the phagocytosis and spreading rates by the mononuclear phagocytes, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) release by leukocytes from healthy and infected mammary glands. Thus, 94 milk samples were divided according the results of the bacteriological analysis and the somatic cell count (SCC). No significant difference was found in cell viability, the phagocytosis and spreading rates by mononuclear phagocytes between the distinct groups. Therefore, the H2O2 release by leukocytes was higher in the milk samples from healthy mammary glands compared to those infected with Streptococcus spp. or Corynebacterium spp. However, when the H2O2 release by phagocytes in 1mL of milk according to SCC mL-1 of each sample was estimated, it was found that milk samples from infected, infected with Staphylococcus spp. and bacteriological negative quarters with high SCC were higher than the healthy ones. It was also observed a positive correlation among SCC and cell viability or phagocytosis and spreading rates, and a negative correlation between H2O2 release and cell viability or SCC. In face of, it can be concluded that the SCC, as well as their function and the cell viability, are related to mammary gland health.
Immune response; macrophages; mastitis; milk