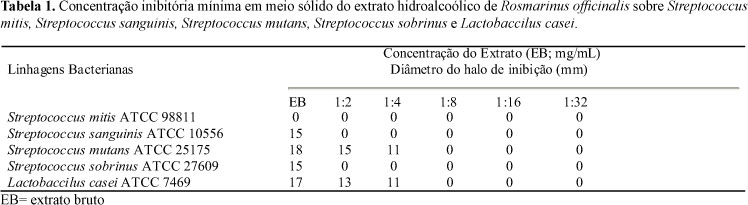
In this study was investigated the antimicrobial activity and in vitro adherence inhibition of a hydro alcoholic Rosmarinus officinalis Linn. (alecrim) on standard strains of Streptococcus mitis ATCC 98811, Streptococcus sanguinis ATCC 10556, Streptococcus mutans ATCC 25175, Streptococcus sobrinus ATCC 27609 and Lactobacillus casei ATCC 7469 extract. The test was carried out by inundation tecniques in Petri dishes to determine the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and inclined tubes techniques the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Adherence to glass (MICA) at the presence of 5% sucrose. Tests with gluconate of chlorexidine 0.12% were performed as controls. MICs of the Rosmarinus officinalis extract dilutions (mg/mL) against S. sanguinis ATCC 10556, S. mutans ATCC 25175, S. sobrinus ATCC 27609 and L. casei ATCC 7469 were 1:1, 1:4, 1:1 e 1:4, respectively. The extract from alecrim inhibited all the standard strains growth tested, except for S. mitis ATCC 98811. MICAs of the Rosmarinus officinalis extract dilutions (mg/mL) against S. mitis ATCC 98811, S. mutans ATCC 25175 e S. sobrinus ATCC were 1:8, 1:16 e 1:8, respectively. The results suggest that there is a possibility of the alecrim use as an oral antimicrobial. Nevertheless, study models which could reproduce situations similar to those seen in bucal caries are necessary for the antimicrobial agents evaluation in the treatment and biofilm dependant oral infections prevention.
Rosmarinus officinalis; Labiatae; antimicrobial activity; antiadherent effect; planktonic bacteria; Streptococcus