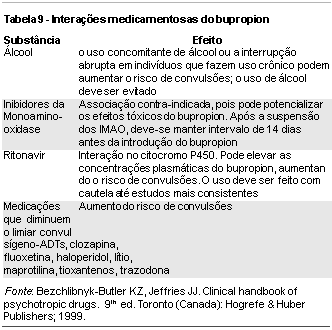
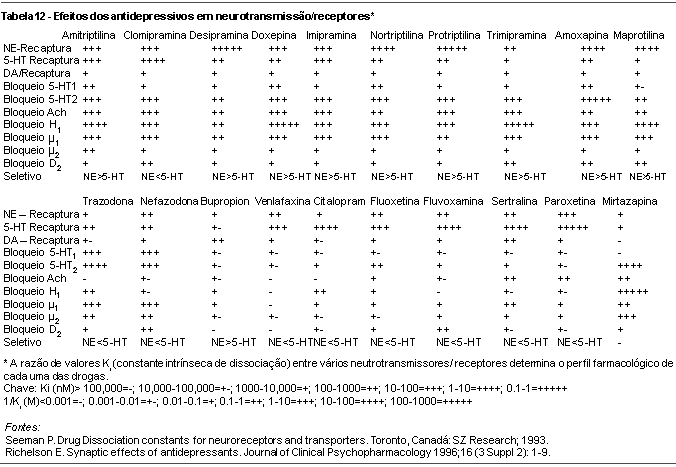
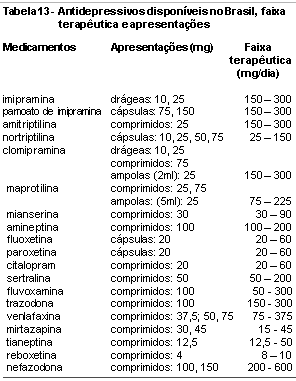
Antidepressant drugs turned depression into a treatable medical problem. In the last five decades, the psychopharmacology of depression has evolved rapidly. Early antidepressants - tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) - were discovered through clinical observation. The TCAs exhibited good antidepressant efficacy due to the enhancement in serotonin and norepinephrine availability. Its use was limited because of unwanted side effects and toxicity risk related to the blockade of histaminergic, cholinergic and alfa-adrenergic receptors. MAOIs can interact with tyramine to cause potentially lethal hypertension and present potentially dangerous interactions with various medications and over-the-counter drugs. The new generation of antidepressants includes the single-receptor selective serotonin or norepinephrine inhibitors and the multiple-receptor-acting antidepressants, such as venlafaxine, bupropion, trazodone, nefazodone, and mirtazapine. They do not act on other receptor sites not related to depression (such as histamine or acetilcholine). This paper reviews the pharmacology of antidepressants, including its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, side effects and drug-drug interactions.
Psychopharmacology; antidepressants; mechanism of action; side effects; pharmacokinetics; drug interactions