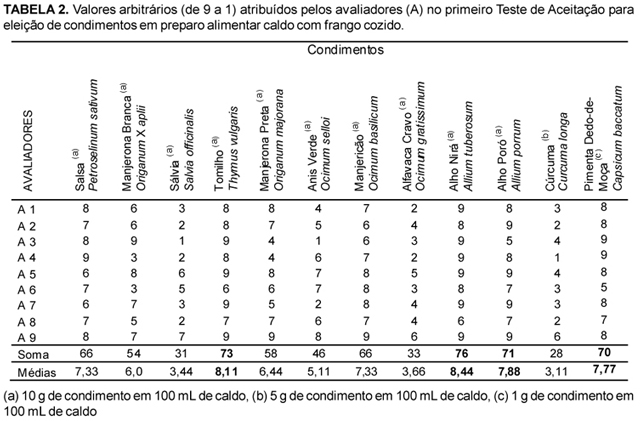
Based on the in vitro antibacterial activity predetermined for 12 spice plants with ethnographic indicator, this feature was tested in loco in the model cooked chicken broth. First, ten evaluators were trained, according to the current legislation for Free and Informed Consent, providing previous knowledge about the plants parsley (Petroselinum sativum), marjoram (Origanum X aplii and Origanum majorana), basil (Ocimum basilicum), common sage (Salvia officinalis), thyme (Thymus vulgaris), anis-like spice (Ocimum selloi), african basilicum (Ocimum gratissimum), nirá garlic (Allium tuberosum), leek (Allium porrum), turmeric (Curcuma longa) and "dedo-de-moça" chili (Capsicum baccatum). Those spices were individually added to the chicken broth to perform a Hedonic Scale-like Acceptance Test, selecting four of the twelve spices that had higher sensory acceptance, "dedo-de-moça" chili, nirá garlic, leek and thyme. A new Acceptance Test was then performed using low, medium and high concentrations of those four spices to establish the most acceptable sensory intensities. The elected quantities (0.5 g "dedo-de-moça" chili, 15 g nirá garlic, 15 g leek and 5 g thyme) were added to the chicken broth, then challenged with Escherichia coli (ATCC 11229) at a final 10 concentration of CFU/mL, the tolerated limit according to legislation. The control group was chicken broth without spices. The bacterial growth was measured at every two hours after the inoculation until 24 hours of confront were completed, using a selective medium for thermo-resistant coliforms, under constant incubation at 25ºC in DBO. Arbitrary values were assigned to the logarithmic growth variations. Compared to the control group, all the spiced treatments individually presented significant antibacterial activity, although the latter was not significant when treatments were compared with each other. However, as regards the antibacterial activity starting time, "dedo-de-moça" chili had the best results, whereas nirá garlic had the best results as regard the extension of this activity time. The 12 studied spice plants had their sensorial characteristics attested, and the four plants that had the best results had proved in loco anti-thermo-resistant coliform activity. Different spice plants were capable of providing sensory and sanitary qualification in chicken broth, under domestic conditions of manipulation.
spicy chicken; sensory evaluation; antibacterial analysis; fecal coliforms