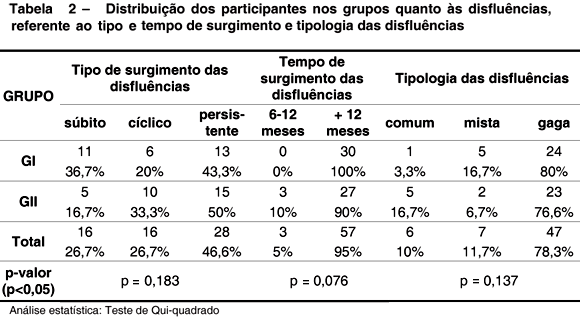
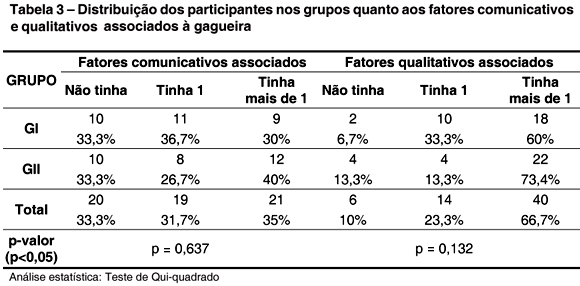
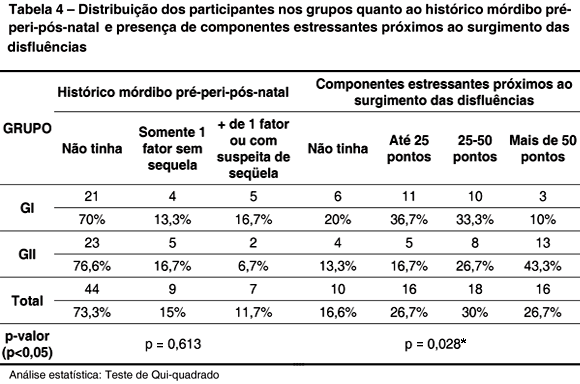
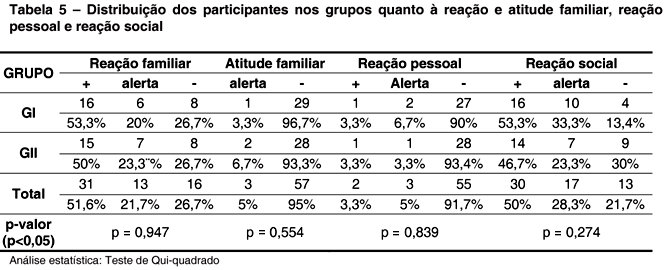
PURPOSE: to investigate and compare the risk factors for stuttering between children with familial developmental stuttering and children with sporadic developmental stuttering. METHODS: 60 children of both genders with stuttering took part, divided in two groups: GI - 30 children with familial developmental stuttering; GII - 30 children with sporadic developmental stuttering. Data were gathered through the Protocol of Risk for the Developmental Stuttering - PRGD (Andrade, 2006), which considers the following factors: age; gender; manner of onset and time of duration for the disfluencies; typology of the disfluencies; associated communicative and qualitative factors; physical and emotional stress; family history concerning stuttering; personal, familiar and social reaction, and familiar attitudes. RESULTS: when Group I (GI) was compared to Group II (GII), the only statically difference was related to emotional stress that occurred near the onset of the disorder. CONCLUSION: the results confirm the complexity of stuttering, as well as the need for investigating the risk factors for this disorder in order to improve the understanding of its possible etiologies.
Stuttering; Risk Factors; Genetics; Speech, Language and Hearing Sciences