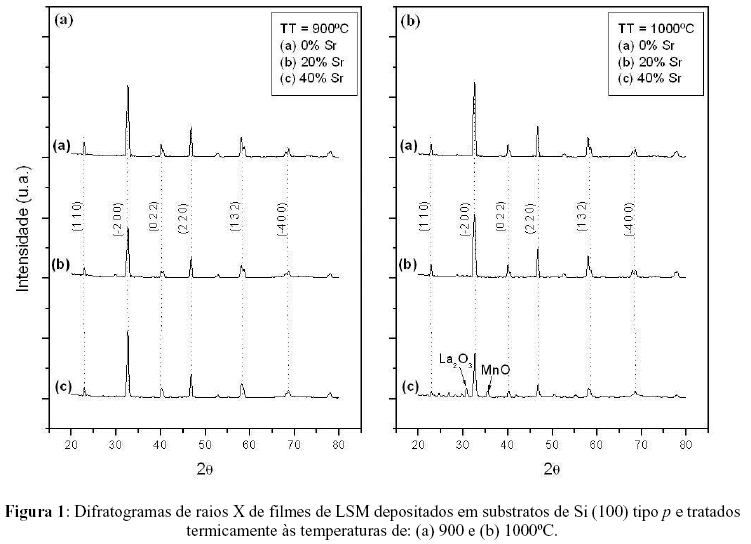
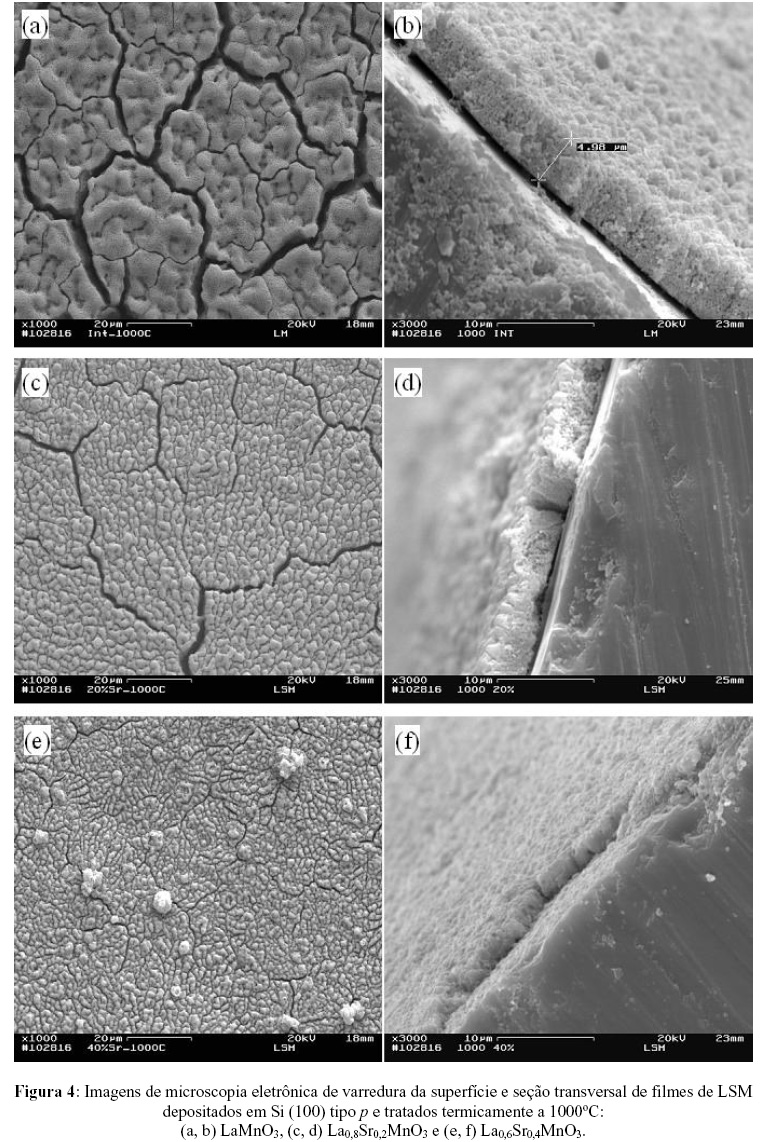
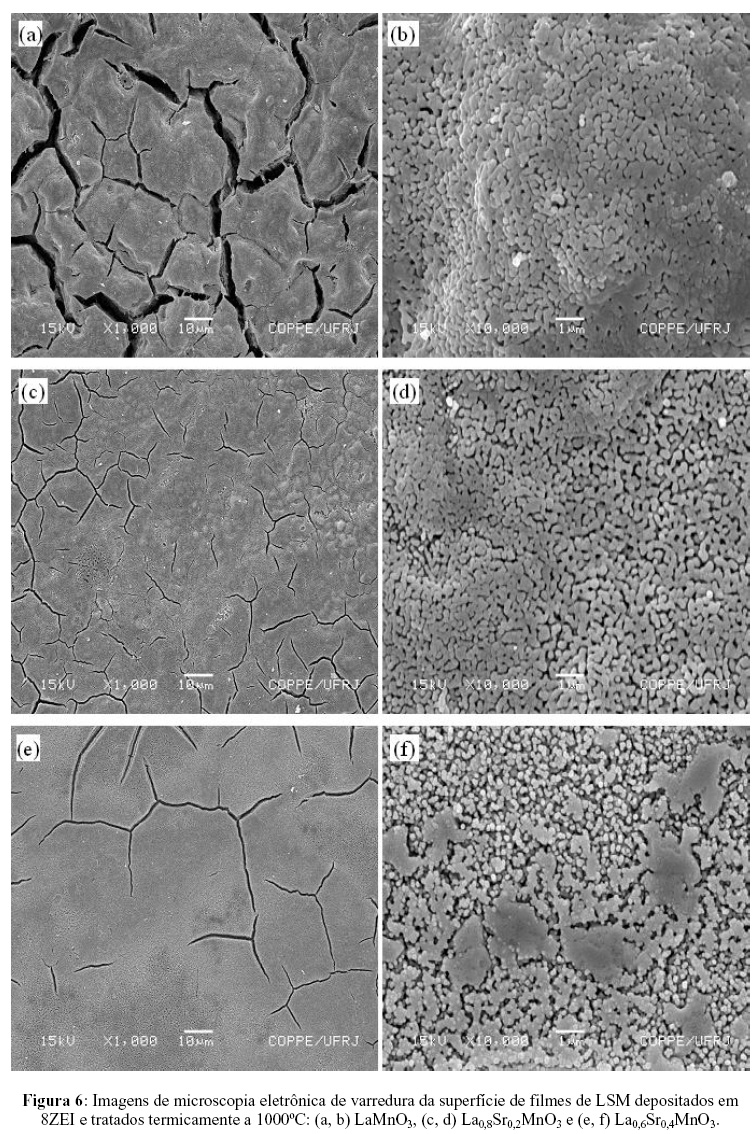
Lanthanum manganite films doped with strontium (LSM) were deposited by spray-pyrolysis on p-type monocrystalline silicon (100) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) 8mol% substrates, aiming their application as cathode in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). The films were heat treated in air at 900 or 1000ºC for two hours and the structural and morphological properties were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results obtained by SEM revealed that the substrate type has great influence on the film microstructure. SEM images of the heat-treated films deposited on silicon substrates tend to present a great amount of cracks. This result is related with the thermal incompatibility between film and substrate, caused by the great difference of the respective thermal expansion coefficients. For films deposited on YSZ substrates better uniformity and adherence were observed. X-ray diffraction patterns of the thermal treated films revealed peaks corresponding to the perovskite structure.
Spray-pyrolysis; film; LSM; SOFC; cathode