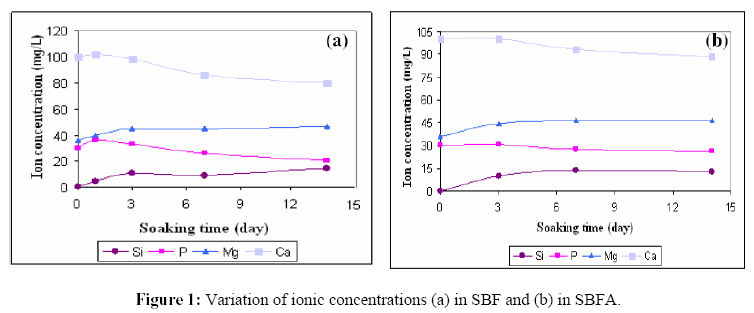
A new composite of poly(methyl methacrylate) - co -(ethyl-hexyl-acrylate) filled with glass of composition (wt.%) 61,33% 3CaO.P2O5 - 23,03% SiO2 - 15,64% MgO was developed. The formation of CaP (calcium phosphate) layers on implants is crucial for their integration in bone. Simulated biological fluids to study in vitro formation of those layers do not usually contain important organic substances, such as proteins. In the present work in vitro bioactivity was studied in a simulated body fluid in presence (SBFA) and in absence of albumin (SBF). The effect of protein on calcium phosphate formation was followed by ion concentration analyses (ICP), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy coupled with X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS). The results showed the precipitation of a CaP layer on the composite in SBFA. Further crystallization of this layer, initially amorphous, seems to be hindered by the presence of albumin.
In vitro bioactivity; albumin; PMMA-based composite; calcium phosphate