Abstract
Utilizou-se a técnica de DNA polimórfico amplificado ao acaso (RAPD) para a análise de 14 amostras de Haemonchus, um tricostrongilídeo parasito do abomaso de bovinos, originárias de diferentes regiões do estado de Minas Gerais. Os perfis foram obtidos utilizando-se cinco iniciadores diferentes. Não houve correlação entre polimorfismo observado com a origem do animal ou com a espécie de Haemonchus estudada.
bovino; RAPD; Haemonchus; DNA
bovino; RAPD; Haemonchus; DNA
cattle; RAPD; Haemonchus; DNA
COMMUNICATION
Randon amplified polymorphic DNA in the analysis of isolates of Haemonchus (Nematoda-Trichostrongylidae) originated from bovines from different regions
DNA polimórfico amplificado ao acaso na análise de isolados de Haemonchus (Nematoda-Trichostrongylidae) originários de bovinos de diferentes regiões
M.P. Guimarães; M.A. Gomes; M.C. Caldeira
Instituto de Ciências Biológicas UFMG Caixa Postal 486 31270-901 - Belo Horizonte, MG
Keywords: cattle, RAPD, Haemonchus, DNA
RESUMO
Utilizou-se a técnica de DNA polimórfico amplificado ao acaso (RAPD) para a análise de 14 amostras de Haemonchus, um tricostrongilídeo parasito do abomaso de bovinos, originárias de diferentes regiões do estado de Minas Gerais. Os perfis foram obtidos utilizando-se cinco iniciadores diferentes. Não houve correlação entre polimorfismo observado com a origem do animal ou com a espécie de Haemonchus estudada.
Palavras-chave: bovino, RAPD, Haemonchus, DNA
Nematodes of the genus Haemonchus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae) are parasites of the abomasum of ruminants. Two species occur in Brazil, H. placei and H. similis (Costa et al. 1986). Distinction between H. contortus and H. placei is difficult (Stevenson et al. 1995, Lichtenfels et al., 1994), and the two species are considered morphologically identical by some authors (Gibbons 1979). There is considerable controversy related to the criteria used to identify these nematodes. The genetic variability using the random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique was estimated by individual intra- and inter-specific genetic markers from samples of H. placei and H. similis. Male worms were collected from natural infections of calves in Florestal, Açucena, Governador Valadares, Carandaí and Janaúba, Minas Gerais State. Samples of H. contortus from naturally infected populations of ovines from Pelotas, Rio Grande do Sul, were used for comparison.
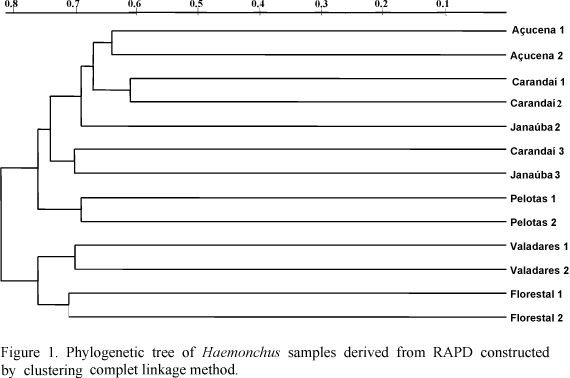
The DNA was obtained using a Nucleon® (Amershan-Pharmacia). The genetic distances between the strains (Link et al., 1995) were listed in two matrixes and used to construct dendrograms (Van de Peer et al., 1994) (Fig. 1). Three topologies were established according to the clustering complete linkage method with the data presented in the matrixes. The complete linkage type of cluster analysis allowed simultaneous comparison of intraspecific patterns. The RAPD generated polymorphic, reproducible patterns for the 14 samples of Haemonchus were analyzed. These profiles were obtained using five different primers (RD5 ATC TGG TTG ATC CTG CCA GT; RD5 ATC CTT CCg Cag gTT CAC CT; SRP3 ggA CTT gAT gCA gCA TCA Agg T; SRP5 gCT AgT CCT gAA Aag CTT gAA gAA gCT; SS65 ggT CTC AAA AAA CCC Acg Ag) for greater discrimination among the samples. The number of bands observed with the five primers was 442. Nevertheless, the polymorphism observed could not be correlated with the origin of the animal or the Haemonchus species studied. Adult helminths either for ovines from Rio Grande do Sul or for bovines from several regions of Minas Gerais, were observed in the same animal. The intra- and interspecific genetic distances were large and did not show important differences. Primers with 10nt generated more polymorphic profiles than larger primers in agreement with Humbert and Cabaret (1995), suggesting the method is not usefull to analyse phylogenetic relationships among individuals of this genus. The RAPD was used to separate the species H. placei, H. contortus and H. longistipes into three groups, but the non-discriminating results were probably due to the primers. Helminths individuals did not show large variability in genetic profile for any smaller primers used, although, independently of the size, products of certain primers did not show great polymorphism among different individuals. The large number of bands observed suggests that this is not an appropriate technique for phylogenetic studies of this genus. However, the amplicons generated by RAPD may have provided individual markers that could be used in the identification of samples preserved in the laboratory for a wide variety of studies.
Recebido em 1 de fevereiro de 2005.
Aceito em 27 de outubro de 2005.
Apoio: FAPEMIG
E-mail: pezzi@icb.ufmg.br
- COSTA, H.M.A.; LEITE, A.C.R.; GUIMARAES, M.P. et al. Distribuição de helmintos parasitos de animais domésticos no Brasil. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., 38, p.465-579, 1986.
- GIBBONS, L.M. Revision of the genus Haemonchus Cobb, 1898 (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae). Syst. Parasitol., v.1, p.3-24, 1979.
- HUMBERT, J.F.; CABARET, J. Use of the random amplified polymorphic DNA for identification of ruminant trichostrongylid nematodes. Parasitol. Res., v.81, p.1-5, 1995.
- LICHTENFELS, J.R.; PILITT, P.A.; HOBERG, E.P. New morphological characters for identifying individual specimens of Haemonchus spp. (Nematoda: Trichostrongyloidea) and a key to species in ruminants of North America. J. Parasitol., v.80, p.107-119, 1994.
- LINK, W.; DIXKENS, C.; SINGH, M. et al. Genetic diversity in European and Mediterranean faba bean germ plasm revealed by RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet., v.90, p.27-32, 1995.
- STEVENSON, L.A.; CHILTON, N.B.; GASSER, R.B. Differentiation of Haemonchus placei from H.contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae) by the ribosomal DNA second internal transcribed spacer. Int. J. Parasitol, v.25, p,483-488, 1995.
- VAN DE PEER, Y.; DE WATCHTER, R. TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput. Appl. Biosci., v.10, p.569-570, 1994.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
19 Apr 2006 -
Date of issue
Feb 2006
History
-
Accepted
27 Oct 2005 -
Received
01 Feb 2005