Abstract
In this study crashworthiness optimization of nested and concentric circular tubes under impact loading is performed by coupling Finite Element model, Response Surface Models and Genetic Algorithm. Specific Energy Absorption (SEA) and Crash Force Efficiency (CFE) are used in crashworthiness optimization since these criteria are important indicators for evaluating crashworthiness performance. Length and thickness of three concentric tubes as well as radius of one tube are adopted as design variables which are effective parameters on SEA and CFE. To reduce the computational cost of the optimization procedure, simple and computationally cheap Response Surface Models are created to replace finite element analyses in further calculations. The Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm –II (NSGAII) is applied to obtain the Pareto optimal solutions. Optimization results are presented for different selected designs that indicate relative importance of multi-objective functions. Results show that the total weight of the vehicles can be reduced by using nested tubes comparing to single tubes with identical masses. These designs can be adopted for use in practice.
Keywords
Nested tube; response surface method; genetic algorithm; multi-objective optimization; crashworthiness; impact loading
1 INTRODUCTION
Thin walled tubular structures are extensively used in automotive, aerospace and military industries due to their energy absorption capacity for the protection of the passengers, drivers and electronic devices of vehicle. Converting some amount of kinetic energy during collision to the plastic energy prevents passengers and devices from squeezing. Besides, inertial loads, which occur at the beginning of the collision, can be harmful for passengers during dynamic crash.
Axial crushing of thin walled circular tubes made of mild steel was introduced by Alexander (1960) Alexander, J. M. (1960). An approximate analysis of the collapse of thin cylindrical shells under axial loading, The Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics, 13.1: 10-15. as an excellent mechanism for energy absorption. Abramowicz and Jones (1984a Abramowicz, W., Jones, N. (1984a). Dynamic axial crushing of circular tubes, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2.3: 263-281. , 1984b Abramowicz, W., Jones, N. (1984b). Dynamic axial crushing of square tubes, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2.2: 179-208. , and 1986 Abramowicz, W., Jones, N. (1986). Dynamic progressive buckling of circular and square tubes, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 4.4: 243-270. ) investigated the circular and square steel tubes under static and dynamic loading. These tubes absorb and convert large amounts of kinetic energy into plastic strain energy under severe loading conditions. In relation with continuous interest to energy absorption capability of thin walled tubes, Jones (1989 Jones, N. (1989). Recent studies on the dynamic plastic behavior of structures, Applied Mechanics Reviews, 42.4: 95-115. , 1996 Jones, N. (1996). Recent studies on the dynamic plastic behavior of structures-Update, Applied Mechanics Reviews, 49: 112-117. , and 2011 Jones, N. (2011). Structural impact, Cambridge university press. ) reviewed elasto-plastic behavior of structures under impact conditions.
Kim (2002) Kim, H. S. (2002). New extruded multi-cell aluminum profile for maximum crash energy absorption and weight efficiency, Thin-Walled Structures, 40.4: 311-327. firstly studied axial crushing behavior of multi-cell tubes. Zhang et al (2006) Zhang, X., Cheng, G., Zhang, H. (2006). Theoretical prediction and numerical simulation of multi-cell square thin-walled structures, Thin-Walled Structures, 44.11: 1185-1191. showed that the energy absorption of a single-cell tube can be increased by 50% when the section is divided into 3×3 cells and they investigated effect of different parts on the cross section. Najafi and Rais-Rohani (2011) Najafi, A., Rais-Rohani, M. (2011). Mechanics of axial plastic collapse in multi-cell, multi-corner crush tubes, Thin-Walled Structures, 49.1: 1-12. made comparison between analytical and numerical results of axially loaded multi-cell tubes.
Optimization procedure was successfully applied to increase the efficiency of many types of crush structures such as multi-cell tubes ( Kurtaran et al. (2002) Kurtaran, H., Eskandarian, A., Marzougui, D., Bedewi, N. E. (2002). Crashworthiness design optimization using successive response surface approximations, Computational mechanics, 29.4: 409-421. ). For example, Hou et al. (2008) Hou, S., Li, Q., Long, S., Yang, X., Li, W. (2008). Multiobjective optimization of multi-cell sections for the crashworthiness design, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 35.11: 1355-1367. carried out multi-objective optimization of cell tubes by maximizing Specific Energy Absorption (SEA) and minimizing Peak Crush Force (PCF) values. They compared the result of 1-cell, 2-cell, 3-cell and 4-cell tubes with pareto curve.
Yin et al. (2014a Yin, H., Wen, G., Liu, Z., Qing, Q. (2014a). Crashworthiness optimization design for foam-filled multi-cell thin-walled structures, Thin-Walled Structures, 75: 8-17. and 2014b Yin, H., Wen, G., Wu, X., Qing, Q., Hou, S. (2014b). Crashworthiness design of functionally graded foam-filled multi-cell thin-walled structures, Thin-Walled Structures, 85: 142-155. ) investigated foam integration to multi-cell tube system. In different studies researchers suggested analytical solutions for mean crushing force curves of multi-cell tubes ( Zhang et al. (2006)) Zhang, X., Cheng, G., Zhang, H. (2006). Theoretical prediction and numerical simulation of multi-cell square thin-walled structures, Thin-Walled Structures, 44.11: 1185-1191. . Qiu et al. (2016) Qiu, N., Gao, Y., Fang, J., Feng, Z., Sun, G., Li, Q. (2016). Theoretical prediction and optimization of multi-cell hexagonal tubes under axial crashing, Thin-Walled Structures, 102: 111-121. derived analytical solution for multi-cell tubes using Simplified Super Folding Element theory and optimized the cross-sectional dimensions of the hexagonal tubes using multi-objective optimization procedure.
Superior energy absorption capability of multi-cell tubes including nested multi-tubular structures are expressed in the literature. Usta et al. (2015) Usta, F., Eren, Z., Turkmen, H. S., Kazancı, Z., Mecitoglu, Z. (2015). Numerical investigation of stepped concentric crash tubes subjected to axial impact: The effects of number of tubes, Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST), 2015 7th International Conference on. IEEE, 39-43. and Usta and Türkmen (2017) Usta, F., & Türkmen, H. S. (2017). Crash behavior of nested tube structures with various cross sections. In Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST), 8th International Conference on. IEEE, 23-27. conducted parametric analyses to investigate the effects of the number of cross section and the number of nested tubes with gradually changing lengths on axial crushing performance of thin walled structures. An experimental work including quasi-static crush tests of these systems has been conducted by Nia and Chahardoli (2016a) Nia, A. A., Chahardoli, S. (2016a). Mechanical behavior of nested multi-tubular structures under quasi-static axial load, Thin-Walled Structures, 106: 376–89. . Later on, they have applied optimization procedure to nested tubes through response surface approximation ( Nia and Chahardoli (2016b) Nia, A. A., & Chahardoli, S. (2016b). Optimizing the layout of nested three-tube structures in quasi-static axial collapse, Thin-Walled Structures, 107: 169-181. ).
From the literature, it is seen that very limited study is available for crash optimization of nested tubes. Olabi et al. (2008) Olabi, A. G., Morris, E., Hashmi, M. S. J., Gilchrist, M. D. (2008). Optimised design of nested circular tube energy absorbers under lateral impact loading, International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 50.1: 104-116. investigated the effects of the lateral impact on circular nested tube systems and show that optimized nested tubes gave desirable force deflection response compared to standard tube systems. Nia and Chahardoli (2016b) optimized circular nested tube systems with different height and thickness subjected to quasi static crushing. In this study, multi objective optimization procedure is applied to optimize tri-tubular nested and concentric circular tube system by coupling Genetic Algorithm, Response Surface method and Finite Element (FE) model. Specific energy absorption (SEA) and Crush Force Efficiency (CFE) criteria are used in representing multi-objective objective functions and Peak Crush Force (PCF) in constraint function. Response surface models are developed for CFE and SEA of the nested tube structures. By using response surface models, nested tube structure is optimized for optimum crashworthiness performance. This study contributes to the literature an optimum design cluster of nested and concentric tubes regarding to SEA and CFE under dynamic impact loading.
2. FINITE ELEMENT MODEL
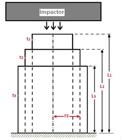
In this study, finite element model of nested and concentric circular tri-tubular system is used in obtaining SEA and CFE responses required in optimization. Nested and concentric circular tri-tubular system employed is shown in Figure 1 . L1, L2 and L3 indicate length of tubes, t1 , t2 and t3 denote thickness of tubes and r2 indicates radius of middle tube.
Nested and concentric circular tri-tubular system is crushed in the axial direction by a 1132 kg rigid mass with a 4.22 m/s initial velocity. The bottom line nodes of all tri-tubes are clamped, while top nodes of the three tubes are constrained except axial direction due to provide deformation behavior. Tubes are modeled by using Belytschko-Lin-Tsay-4-node thin shell elements with three integration points through the thickness and one integration point in the element plane. The element size of 2 x 2 mm is found to be sufficient and suitable to simulate the crushing deformation of tubes (29160 elements, 29491 nodes). Automatic contact algorithms are activated to prevent penetration of tube surfaces after deformation. The static and dynamic friction coefficients are chosen as 0.2 and 0.3 respectively ( Kazancı and Bathe (2012) Kazancı, Z., Bathe, K-J. (2012). Crushing and crashing of tubes with implicit time integration. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 42,:80-88. , Fang et al. (2014) Fang, J., Gao, Y., Sun, G., Zhang, Y., Li, Q. (2014). Parametric analysis and multiobjective optimization for functionally graded foam-filled thin-wall tube under lateral impact, Computational Materials Science, 90: 265-275. ). FE analysis is conducted using commercial code LS-DYNA ( Hallquist (2007) Hallquist, J. O. (2007). LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual, Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 970. ).
In FE analysis, tube system is considered made of Aluminum 6063. Following material properties for Aluminum 6063 is used in this study. Density is ρ = 2700 kg/m3, Young’s modulus is E = 68.2 GPa, initial yield stress is σy= 80 MPa, ultimate stress is σu= 173 MPa, and Poisson’s ratio is ʋ = 0.3.
In order to validate the FE model, FE analysis result of the tri-tubular circular tubes under axial dynamical loading is compared with experimental results as shown in Figure 2 . Experiment is conducted by using drop-tower test facility of the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK). 1132 kg drop weight is released from a height that provides approximately 10 kJ. From comparison, it is seen that FE response is very close to the experimental result and therefore it can be concluded that FE model can be used in producing crush responses used in optimization.
3. OPTIMIZATION PROCEDURE
In order to evaluate the crashworthiness of the thin-walled structures, it is essential to define crashworthiness indicators. Energy Absorption (EA), Specific Energy Absorption (SEA), Mean Crushing Force (MCF) and Crash Force Efficiency (CFE) are usually used as the important indicators for evaluating crashworthiness performance ( Guler et al. (2010) Guler, M. A., Cerit, M. E., Bayram, B., Gerceker, B., Karakaya, E. (2010). The effect of geometrical parameters on the energy absorption characteristics of thin-walled structures under axial impact loading. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 15.4: 377-390. ). Energy absorption of a structure subjected to the axial loading can be expressed as:
where δ is the axial crushing distance and P(s) denotes the axial crushing force. SEA is calculated as energy absorption divided by mass as below
MCF is calculated as absorbed energy divided by axial crushing distance as
CFE is calculated as mean crushing force (Pm) divided by peak crush force (PCF). CFE values close to one are desired for efficient designs.
Details of optimization steps are explained in the following sections.
3.1 Formulation of optimization problem
In this study, optimization of tri-tubular nested and concentric circular tube system is formulated as multi-objective constrained optimization problem. CFE and SEA criteria are used in expressing objective functions expressed as f1 and f2 successively. For optimum crashworthiness design, objective functions are desired to be maximized.
In multi-objective optimization procedure adopted in this study, multi objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) method is used. Considering multi-objective and constraint functions, optimization problem is formulated as below:
subject to
3.2 Response surface models for optimization criteria
In order to reduce the computational cost of the optimization problem with many design variables, simple approximate models are used to replace the costly original objective and constraint functions, which are calculated using expensive FE analysis. Simple approximate models are often referred to as Response Surface (RS) models and are obtained using Response Surface Method (RSM). In this study, RS models are used for SEA and CFE criteria during optimization. RSM was originally developed for the model fitting of physical experiments by Box and Draper (1987) Box, G. E., Draper, N. R. (1987). Empirical model-building and response surfaces (Vol. 424), New York: Wiley. and later adopted in other fields.
In RSM, polynomial model is selected first to approximate the actual function. Often quadratic polynomial models are selected. Quadratic models can be written as
where xi are variables that the function depends on. c0, ci and cij are tuning parameters and n is the number of variables. Then, Design of Experiment (DOE) method is selected according to the order of polynomial function and the number of design variables. Full Factorial DOE is a good choice for few design variables. For large number of design variables, often a subset of Full Factorial DOE is selected using a suitable selection criterion such as D-optimality selection criterion. Then, FE analyses corresponding to DOE table are conducted to calculate function values. Finally, polynomial model is fitted to the created data set corresponding to DOE table using least-squares method. Steps of RSM is summarized in Figure 3 . Flowchart of optimization procedure adopted in this study is shown in Figure 4 .
In this study a subset of three-level Full Factorial DOE is selected using D-optimality criterion. Subset includes 45 experiments, which is sufficient enough to fit a quadratic function for 7 variables. To implement RSM, a MATLAB code is written.
Ranges of design variables used in creating DOE table are shown in Table 1 . Resulting DOE table and corresponding function values for SEA and CFE criteria are given in Table 2 .
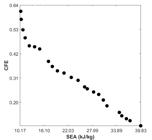
Fitted values and actual values (FE results) for SEA and CFE are compared in Figures 5 - 6 . From Figures 5 - 6 it is seen that good correlation exists between RS model and FE results. Therefore, RS models can be used in the optimization for concentric circular tri-tubular system.
3.3. Solution of optimization problem
Optimization problem formulated in Equations 6 and 7 is solved using Genetic Algorithm (GA).
GA is coupled with the RS models to yield a global optimum as shown in Figure 7 . The GA solves the optimization problem by simulating the biological evolution process based on Darwin’s theory of survival of the fittest. First, a set of potential solutions referred to as population or chromosomes is selected. New and improved solutions are then generated using the previous solutions based on crossover and mutation technique. This process repeats until optimum values are reached. The critical parameters in GAs are the size of the population, cross over rate, mutation rate and number of generations. Detailed information about GA can be found in Ref. ( Goldberg (1989) Goldberg, D. E. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning, 1989, Reading: Addison-Wesley. ).
The Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm –II (NSGAII) is applied to obtain the Pareto optimal solutions ( Deb (2002) Deb, K. (2002). A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II, IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 6.2: 182-197. ). Table 3 indicates the values of NSGAII parameters for considered problem which provides results with good repeatability.
3.4. Optimization results
In this section, multi-objective optimization results of concentric circular tri-tubular system are presented for different CFE and SEA values. Multi optimization method provides Pareto optimal sets for nested and concentric circular tubes. The Pareto optimal frontier provides a set of solutions according to CFE and SEA values, shown graphically in Figure 8 .
Solution of optimization problem expressed in Equations 6 and 7 is conducted with GA. Optimum values of design variables found are shown in Table 4 . In Table 4 , SEA and CFE values at optimum are compared for RS model and FE analysis. Undeformed and deformed shapes of optimum tube structures under impact for different SEA and CFE values, are demonstrated in Figure 9 .
Results show that SEA and CFE values obtained from optimization models and FE analyses are sufficiently close. It indicates that quadratic polynomial function is accurate enough for concentric circular tri-tubular structures. CFE values from optimization result are lower than the values from FE analyses and SEA values are similar for all optimum designs.
In Table 4 , it is seen that the values of optimum design lengths, thicknesses and radius change according to SEA and CFE values. The innermost tube tends to increase with the higher SEA and lower CFE from 150 to 200 mm. On the other hand, the length of outmost tube becomes lower for higher SEA and lower CFE. Besides, the thickness of each tube becomes higher values with the increase of SEA and reduction of CFE. The results prove that optimum designs show a tendency to reduce weight of the tube systems due to obtaining better SEA results. The radius of middle tube which is another design parameter becomes nearly at limit values 23 and 32 mm for each designs.
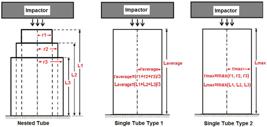
Crash tubes are used traditionally as single tube structures in automotive industry. Therefore, results of optimum designs of nested tubes structures are compared with the results of two different types of single tube structures in Table 5 . In Table 5 , single tubes corresponding to a design number have identical mass values. In Single Tube Type 1, radius and length values correspond to average values in those of nested tubes shown in Figure 10 . In Single Tube Type 2, radius and length values correspond to maximum values in those of nested tubes.
In comparison with the results, nested tubes give higher CFE values only for a few designs. The axial displacement and peak crash force values should be lower to obtain higher CFE values. It can be said that the stiffness of nested tubes should be increased to prevent more deflection in axial direction and the gaps between the tubes should be increased to reduce contact forces.
On the other hand, SEA values of each type are similar. SEA values of Nested Tubes are higher than Single Tube Type 1 and 2. The results show that nested tubes have more advantages in terms of SEA values. Therefore, total weight of the structure can be reduced by using nested tube structures.
4. CONCLUSION
In this study, optimization was carried out in order to improve the crashworthiness performance of nested and concentric circular tubes. SEA and CFE were considered as performance measure for crashworthiness. Specific Energy Absorption and Crash Force Efficiency were calculated using Explicit Finite Element analysis. For further calculations in optimization procedure, FE Analyses were replaced with RS models in order to reduce the computational cost. RS models for SEA and CFE were coupled with Genetic Algorithm to find optimum design variables and multi-objective optimization procedure was performed to maximize the objective function of SEA and CFE. NSGAII was applied to obtain the Pareto optimal solutions and the Pareto optimal frontier was plotted. Length and thickness of three concentric tubes as well as radius of one tube were considered as design variables.
25 different optimum crash tube models were obtained by using multi objective optimization method. SEA and CFE values of optimum designs of nested tube structures were compared with the results of two different types of circular tube structures having identical masses. From design point of view, it was observed that nested tubes had no advantages according to single tubes for CFE criterion. To increase the CFE values of nested tube structures, the stiffness of each tube and the gaps between nested tubes should be increased.
On the other hand, optimum designs gave better results than the single tube types in terms of SEA values. Therefore, nested tubes could provide lower weight to the vehicles.
Acknowledgment
Support for this work has been provided by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under Project Number 113M395.
We thank V. Martínez-Cagigal for the MOPSO code implementation, which can be found in https://es.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/62074-multi-objective-particle-swarm-optimization--mopso-?focused=7573906&tab=function .
References
- Abramowicz, W., Jones, N. (1984a). Dynamic axial crushing of circular tubes, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2.3: 263-281.
- Abramowicz, W., Jones, N. (1984b). Dynamic axial crushing of square tubes, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2.2: 179-208.
- Abramowicz, W., Jones, N. (1986). Dynamic progressive buckling of circular and square tubes, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 4.4: 243-270.
- Alexander, J. M. (1960). An approximate analysis of the collapse of thin cylindrical shells under axial loading, The Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics, 13.1: 10-15.
- Box, G. E., Draper, N. R. (1987). Empirical model-building and response surfaces (Vol. 424), New York: Wiley.
- Deb, K. (2002). A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II, IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 6.2: 182-197.
- Fang, J., Gao, Y., Sun, G., Zhang, Y., Li, Q. (2014). Parametric analysis and multiobjective optimization for functionally graded foam-filled thin-wall tube under lateral impact, Computational Materials Science, 90: 265-275.
- Goldberg, D. E. (1989). Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning, 1989, Reading: Addison-Wesley.
- Guler, M. A., Cerit, M. E., Bayram, B., Gerceker, B., Karakaya, E. (2010). The effect of geometrical parameters on the energy absorption characteristics of thin-walled structures under axial impact loading. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 15.4: 377-390.
- Hallquist, J. O. (2007). LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual, Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 970.
- Hou, S., Li, Q., Long, S., Yang, X., Li, W. (2008). Multiobjective optimization of multi-cell sections for the crashworthiness design, International Journal of Impact Engineering, 35.11: 1355-1367.
- Jones, N. (1989). Recent studies on the dynamic plastic behavior of structures, Applied Mechanics Reviews, 42.4: 95-115.
- Jones, N. (1996). Recent studies on the dynamic plastic behavior of structures-Update, Applied Mechanics Reviews, 49: 112-117.
- Jones, N. (2011). Structural impact, Cambridge university press.
- Kazancı, Z., Bathe, K-J. (2012). Crushing and crashing of tubes with implicit time integration. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 42,:80-88.
- Kim, H. S. (2002). New extruded multi-cell aluminum profile for maximum crash energy absorption and weight efficiency, Thin-Walled Structures, 40.4: 311-327.
- Kurtaran, H., Eskandarian, A., Marzougui, D., Bedewi, N. E. (2002). Crashworthiness design optimization using successive response surface approximations, Computational mechanics, 29.4: 409-421.
- Najafi, A., Rais-Rohani, M. (2011). Mechanics of axial plastic collapse in multi-cell, multi-corner crush tubes, Thin-Walled Structures, 49.1: 1-12.
- Nia, A. A., Chahardoli, S. (2016a). Mechanical behavior of nested multi-tubular structures under quasi-static axial load, Thin-Walled Structures, 106: 376–89.
- Nia, A. A., & Chahardoli, S. (2016b). Optimizing the layout of nested three-tube structures in quasi-static axial collapse, Thin-Walled Structures, 107: 169-181.
- Olabi, A. G., Morris, E., Hashmi, M. S. J., Gilchrist, M. D. (2008). Optimised design of nested circular tube energy absorbers under lateral impact loading, International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 50.1: 104-116.
- Qiu, N., Gao, Y., Fang, J., Feng, Z., Sun, G., Li, Q. (2016). Theoretical prediction and optimization of multi-cell hexagonal tubes under axial crashing, Thin-Walled Structures, 102: 111-121.
- Usta, F., Eren, Z., Turkmen, H. S., Kazancı, Z., Mecitoglu, Z. (2015). Numerical investigation of stepped concentric crash tubes subjected to axial impact: The effects of number of tubes, Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST), 2015 7th International Conference on. IEEE, 39-43.
- Usta, F., & Türkmen, H. S. (2017). Crash behavior of nested tube structures with various cross sections. In Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST), 8th International Conference on. IEEE, 23-27.
- Yin, H., Wen, G., Liu, Z., Qing, Q. (2014a). Crashworthiness optimization design for foam-filled multi-cell thin-walled structures, Thin-Walled Structures, 75: 8-17.
- Yin, H., Wen, G., Wu, X., Qing, Q., Hou, S. (2014b). Crashworthiness design of functionally graded foam-filled multi-cell thin-walled structures, Thin-Walled Structures, 85: 142-155.
- Zhang, X., Cheng, G., Zhang, H. (2006). Theoretical prediction and numerical simulation of multi-cell square thin-walled structures, Thin-Walled Structures, 44.11: 1185-1191.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
14 June 2018 -
Date of issue
2018
History
-
Received
09 Aug 2017 -
Reviewed
14 Jan 2018 -
Accepted
23 Jan 2018