Abstract
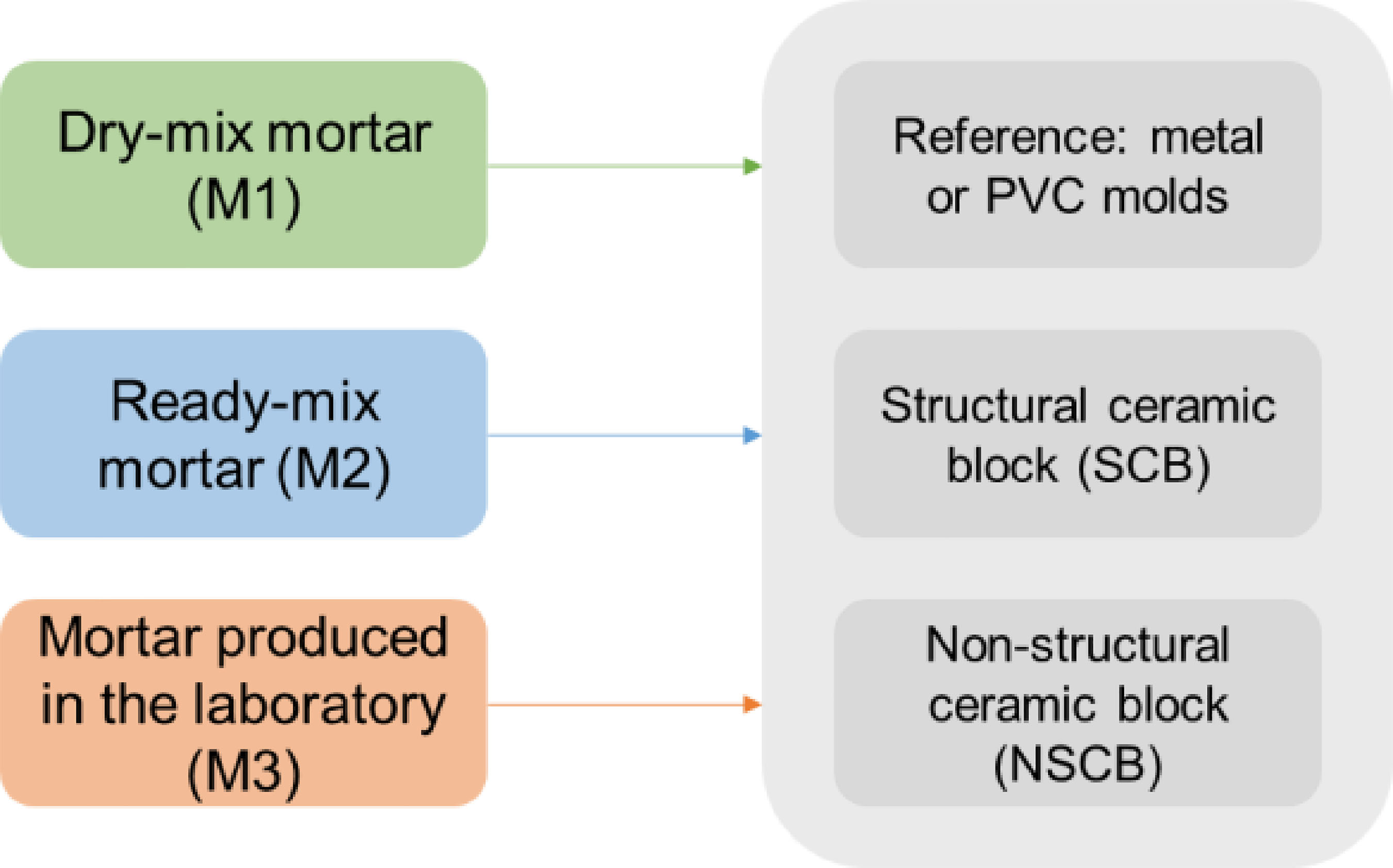
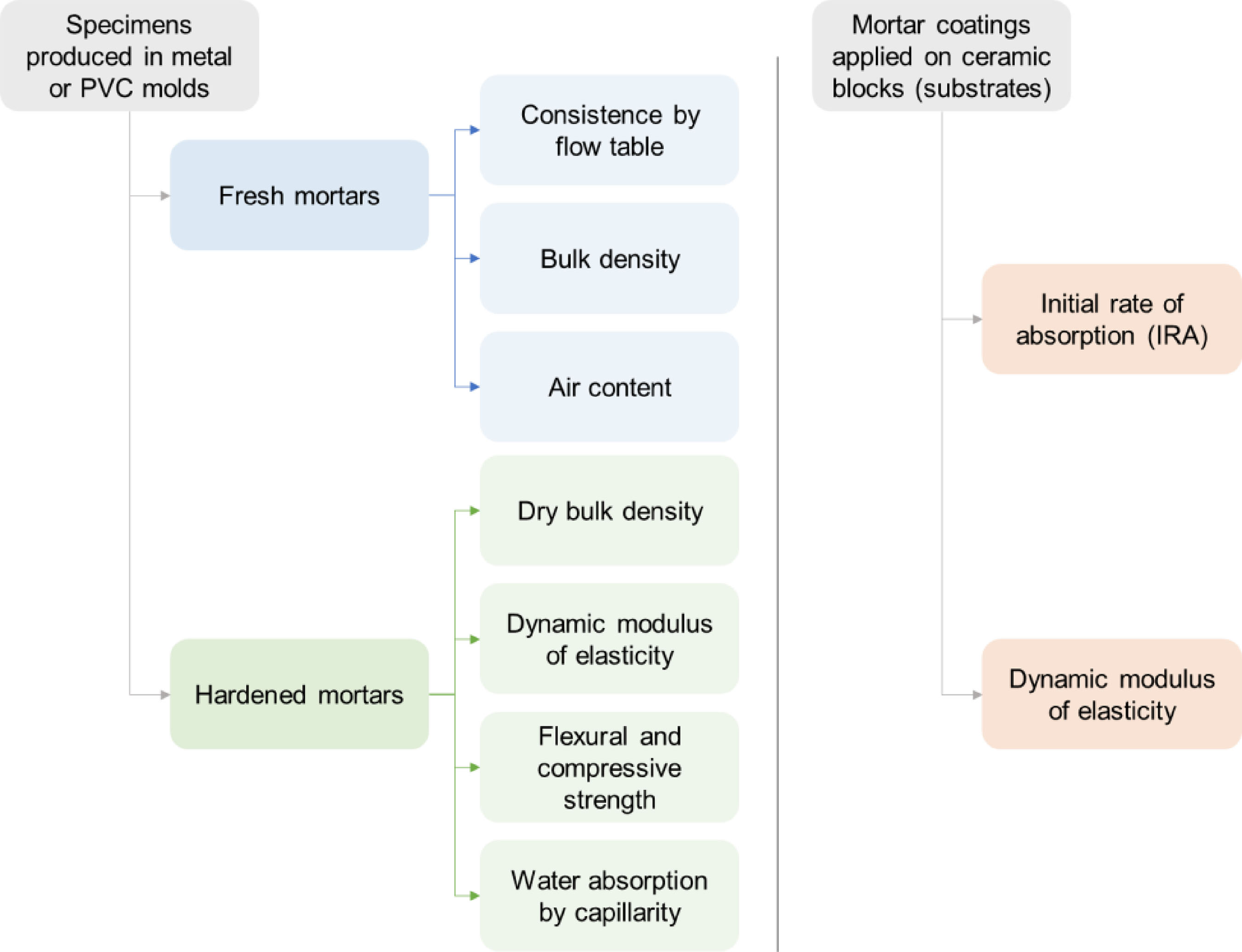
The characteristics of masonry substrates affect rendering mortar performance. This study compares three mortar types (dry-mix, ready-mix, and mortar produced in the laboratory) applied to two types of ceramic blocks differing in Initial Rate of Absorption (IRA) and cast in metal/PVC molds. Mortars were characterized in the fresh and hardened states, and their IRA and dynamic modulus of elasticity were determined after application onto the blocks. While the ready-mix mortar had the highest variation on IRA results depending on the substrate, for the mortar produced in the laboratory, using structural or non-structural blocks did not make a difference. Mortar and substrate types influenced the modulus of elasticity, with values rising from the ready-mix mortar to the dry-mix and that produced in the laboratory. Mortars on ceramic blocks had higher modulus than those in metal molds. Further studies are recommended on porosity, non-absorbent substrates, lateral waterproofing, and potential wave transmission through the substrate.
Keywords
Rendering mortar; Ceramic block; Substrate influence; Initial rate of absorption; Dynamic modulus of elasticity

 Influence of two ceramic substrates on water absorption and modulus of elasticity of rendering mortars
Influence of two ceramic substrates on water absorption and modulus of elasticity of rendering mortars Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
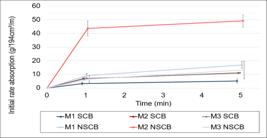 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail