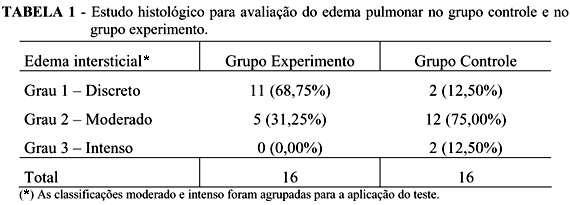
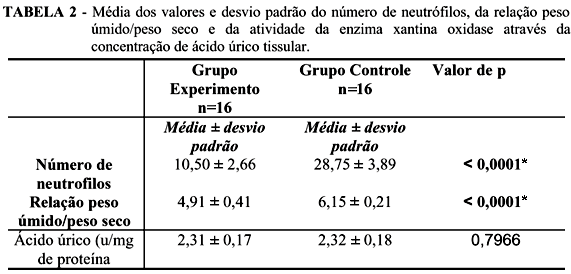
PURPOSE: To study the role of methylene blue as an inibitor of superoxide production by xantine oxidase. METHODS: Thirty two Wistar rats were divided in 2 groups of 16 animals: the control group and the experimental group. All the animals were submitted to a laparotomy for the occlusion of the cranial mesenteric artery during 60 minutes. The reperfusion was confirmed by the 'pulsation of the artery after releasing the temporary ligature. In the animals of the control group, 2 ml of saline were injected in the peritoneal cavity and in the animals of the experimental group 2 ml of methylene blue were injected in the peritoneal cavity. After reperfusion for 4 hours, the animals were sacrificed. The lungs were excised for histological studies, for evaluation of the pulmonary edema and the activity of xantine oxidase. RESULTS: In the animals of the experimental group the inflammatory lesion of the lung was grater in the control group as well as the edema. The activity of the xantine oxidase was similar in both groups. CONCLUSION: In rats, methylene blue can protect the lung against the toxic effects of oxygen radical in ischemia-reperfusion injuries.
Methylene blue; Ischemia-reperfusion injury; Lung