Introduction
Lemierre's syndrome consists of a pharyngeal infection associated with septicemia and internal jugular thrombosis with septic emboli. This condition was described in 1936 by Andre Lemierre.11. Lemierre A. On certain septicemias due to anaerobic organisms. Lancet. 1936;227:701-3.and22. Gupta T, Parikh K, Puri S, Agrawal S, Agrawal N, Sharma D, et al. The forgotten disease: bilateral Lemierre's disease with mycotic aneurysm of the vertebral artery. Am J Case Rep. 2014;15:230-4. It was initially named as post-anginal septicemia, and then, "forgotten disease", by becoming a rare condition after the advent of antibiotics, with fewer than 100 cases reported since 1974.22. Gupta T, Parikh K, Puri S, Agrawal S, Agrawal N, Sharma D, et al. The forgotten disease: bilateral Lemierre's disease with mycotic aneurysm of the vertebral artery. Am J Case Rep. 2014;15:230-4. Lamierre's syndrome has also been named necrobacillosis, due to the presence of Fusobacterium necrophorum, a commensal bacteria from oral cavity which is considered the most common causative agent of the disease. Bacteroides, Streptococcus group B and C,Streptococcus oralis, Staphylococcus epidermitis, Enterococcusand Proteus mirabilis may also be involved. 33. Vargiami EG, Zafeiriou DI. Eponym: the Lemierre syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169:411-4.
The objective of this report is to present a Lemierre's-syndrome case treated at the Otorhinolaryngology Emergency Room.
Case presentation
Male patient, aged 18 years, presented initially with throat pain and left-side neck pain evolving with fever (37.8 °C). This patient had been treated with benzathine penicillin and symptomatic medication. On the 4th day, he began to experience pain in his knees and ankles.
At admission, the patient was in poor general condition, with paleness, dehydration, tachycardia (116 bpm), with 95% saturation in room air, hypotensive (108 × 57 mmHg) and afebrile (36.6 °C). The patient presented with hyperemic oropharyngeal examination, a left cervical bulging, hepatomegaly and bilateral edema and hyperemia in his ankles. The initial investigation showed thrombocytopenia (28,000/mm3), leukocytosis with a left shift (16,100/mm3), increased creatinine (3.5 mg/dL) and urea (243 mg/dL). The patient was treated according to the protocol for severe sepsis, including blood culture, vigorous hydration, IV ceftriaxone 2 g, and hospitalization.
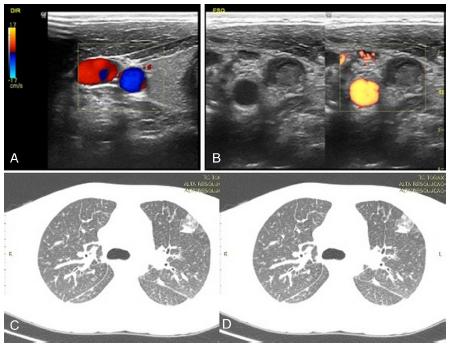
At the investigation for other septic foci, a cervical ultrasound scan showed multiple lymph nodes with inflammatory reaction and thrombosis of upper and middle thirds of left internal jugular vein (Fig. 1A and B). An ultrasound of the lower limbs showed a small bilateral ankle joint effusion.
Right cervical doppler ultrasound scan with normal vascular flow. (B) Flow absent in left internal jugular vein. (C) Computed tomography of chest; lung parenchyma showing multiple nodes. (D) Ground-glass appearance in lung bases.
During the 1st day of hospitalization, the patient exhibited progressive dyspnea, with tachypnea, suprasternal depression and stertor crackes on pulmonary auscultation. We considered that the sepsis had its origin in a pulmonary focus, requiring tracheal intubation. Thoracic CT scan showed pleural effusion and multiple nodules distributed through the lung parenchyma, with areas of a ground-glass pattern corresponding to septic emboli (Fig. 1C and D). After the introduction of piperacillin tazobactam, the patient's evolution was favorable, with improvement of the sepsis. The patient was discharged after 14 days of intravenous antibiotic therapy. Blood cultures showed no bacterial growth.
The initial finding of pharyngeal infection accompanied by sepsis, in combination with confirmation of jugular vein thrombosis and pulmonary septic emboli, validated the hypothesis of Lemierre's syndrome.
Discussion
Lemierre's syndrome occurs predominantly in young adults1; one study reported higher prevalence in men,44. Eykyn SJ. Necrobacillosis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1989;62:41-6. as occurred in this case. In most cases of this syndrome, a pharyngitis is noted before occurrence of systemic complications, similarly to what happened in our case; but the internal jugular thrombosis may result from other head and neck infections.55. Goldenberg NA, Knapp-Clevenger R, Hays T, Manco-Johnson MJ. Lemierre's and Lemierre's-like syndromes in children: survival and thromboembolic outcomes. Pediatrics. 2005;116: e543-8.and66. Eilbert W, Singla N. Lemierre's syndrome. Int J Emerg Med. 2013;6:40. The incidence is estimated to be 3.6 cases per million inhabitants.22. Gupta T, Parikh K, Puri S, Agrawal S, Agrawal N, Sharma D, et al. The forgotten disease: bilateral Lemierre's disease with mycotic aneurysm of the vertebral artery. Am J Case Rep. 2014;15:230-4.
The septic emboli originating from the jugular thrombosis mainly affect lungs and joints,33. Vargiami EG, Zafeiriou DI. Eponym: the Lemierre syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169:411-4. exactly the affected foci in the current report. The lung condition may involve severe chest pain, dyspnea and hemoptysis due to pulmonary abscesses. The joints as well may develop septic arthritis and osteomyelitis.33. Vargiami EG, Zafeiriou DI. Eponym: the Lemierre syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169:411-4.
The treatment of this syndrome consists of support for the sepsis and antibiotic therapy, as was done in this case. Antibiotic therapy should be directed to anaerobes, staphylococci and streptococci. The main etiologic agent, F. necrophorum, is sensitive to penicillin, clindamycin and metronidazole.66. Eilbert W, Singla N. Lemierre's syndrome. Int J Emerg Med. 2013;6:40. The blood culture of our patient showed no bacterial growth; but there is a question: whether the previous use of antibiotics or a failure in the collection procedures for anaerobic organisms may have had some influence on the negative bacterial growth outcome.
Final considerations
Lemierre's syndrome is a rare disease secondary to common otorhinolaryngological infections. The otorhinolaryngologist should be alert for signs of sepsis in common infectious conditions. A correct approach to sepsis is critical for obtaining good results in this syndrome.
References
-
1Lemierre A. On certain septicemias due to anaerobic organisms. Lancet. 1936;227:701-3.
-
2Gupta T, Parikh K, Puri S, Agrawal S, Agrawal N, Sharma D, et al. The forgotten disease: bilateral Lemierre's disease with mycotic aneurysm of the vertebral artery. Am J Case Rep. 2014;15:230-4.
-
3Vargiami EG, Zafeiriou DI. Eponym: the Lemierre syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 2010;169:411-4.
-
4Eykyn SJ. Necrobacillosis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1989;62:41-6.
-
5Goldenberg NA, Knapp-Clevenger R, Hays T, Manco-Johnson MJ. Lemierre's and Lemierre's-like syndromes in children: survival and thromboembolic outcomes. Pediatrics. 2005;116: e543-8.
-
6Eilbert W, Singla N. Lemierre's syndrome. Int J Emerg Med. 2013;6:40.
-
☆
Please cite this article as: Noh HJ, de Freitas CA, de Souza RPSF, Simões JC, Kosugi EM. Lemierre syndrome: a rare complication of pharyngotonsillitis. 2015. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2015;81:568-70.
-
☆☆
Institution: Sector of Rhinology, Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, Escola Paulista de Medicina, Universidade Federal de São Paulo (EPM-UNIFESP), São Paulo, SP, Brazil.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
Sep-Oct 2015
History
-
Received
03 Feb 2015 -
Accepted
16 Mar 2015