Abstracts
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the role, especially of computed tomography, in the staging of maxillary sinus carcinomas. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Ten cases of carcinoma treated in Hospital Heliópolis Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Head and Neck Surgery, São Paulo, SP, Brazil, in the period between 1988 and 2002, were evaluated. RESULTS: Nine patients presented with tumor extension to the cheek, eight to the masticator space, seven to the mouth floor and hard palate, five to the pterygoid fossa, five to the orbit, three to the ethmoid bone, and one to the skull base. Three of the patients were staged T3, and seven T4. Two patients had lymph nodes metastases at their initial presentation, and were staged T4. All of the cases were histopathologically confirmed. CONCLUSION: The accurate analysis of the tumor local extent and dissemination by means of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging plays a relevant role in the surgical planning, besides influencing the therapeutic conduct and prognosis.
Squamous cell carcinoma; X-ray tomography; Cancer; Maxillary sinus
OBJETIVO: Avaliar o papel, principalmente da tomografia computadorizada, no estadiamento dos carcinomas dos seios maxilares. MATERIAIS E MÉTODOS: Foram analisados dez casos de carcinoma diagnosticados e tratados pelos Departamentos de Diagnóstico por Imagem e Cirurgia de Cabeça e Pescoço do Hospital Heliópolis, São Paulo, SP, entre 1988 e 2002. RESULTADOS: Nove pacientes tiveram extensão tumoral para a bochecha, oito para o espaço mastigador, sete para o assoalho da boca e palato duro, cinco para a fossa pterigóide, cinco para a órbita, três para o etmóide e um para a base do crânio. Três pacientes foram classificados como T3 e sete, como T4. Dois tinham metástases linfonodais no momento da apresentação inicial, os quais pertenciam ao estágio T4. Todos os casos foram confirmados com exame histopatológico. CONCLUSÃO: A análise precisa da extensão local e disseminação tumoral fornecida pela tomografia computadorizada e ressonância magnética desempenha papel importante no planejamento cirúrgico, influenciando, também, na conduta terapêutica e prognóstico.
Carcinoma epidermóide; Tomografia por raios X; Câncer; Seio maxilar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Maxillary sinus carcinoma: an analysis of ten cases* Mailing address: Dr. Olger de Souza Tornin Rua Oscar Freire, 1811, ap.106, Pinheiros São Paulo, SP, Brazil 05409-011 E-mail: olger1@uol.com.br
Ricardo Pires de SouzaI; Flamarion de Barros CordeiroII; Fábio Mota GonzalezII; Ilka YamashiroII; Ademar José de Oliveira Paes JuniorIII; Olger de Souza TorninIV; Renato Assayag BotelhoV; Claudia da Costa LeiteVI; Cristiano Ventorim de BarrosVII; Igor Motta de AquinoVIII; Leonardo Lopes de MacedoVIII
IRadiologist, Coordinator for Residency in Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging and Post-Graduation Professor of Health Sciences at Hospital Heliópolis, Doctor in Radiology by Universidade de São Paulo
IIRadiologists, Master Degree in Health Sciences by Hospital Heliópolis
IIIRadiologist, Doctor in Health Sciences by Universidade de São Paulo
IVRadiologist, Master in Health Sciences by Hospital Heliópolis, Professionalizing Practice in Magnetic Resonance Imaging by Universidade de São Paulo
VRadiologist, Master Degree Student in Health Sciences by Hospital Heliópolis
VIRadiologist, Chief for Sector of Magnetic Resonance Imaging at Universidade de São Paulo
VIIRadiologist, Doctorate Student in Sciences by Universidade de São Paulo
VIIIResidents in Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging at Hospital Heliópolis
Mailing address Mailing address: Dr. Olger de Souza Tornin Rua Oscar Freire, 1811, ap.106, Pinheiros São Paulo, SP, Brazil 05409-011 E-mail: olger1@uol.com.br
ABSTRACT
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the role, especially of computed tomography, in the staging of maxillary sinus carcinomas.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Ten cases of carcinoma treated in Hospital Heliópolis Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Head and Neck Surgery, São Paulo, SP, Brazil, in the period between 1988 and 2002, were evaluated.
RESULTS: Nine patients presented with tumor extension to the cheek, eight to the masticator space, seven to the mouth floor and hard palate, five to the pterygoid fossa, five to the orbit, three to the ethmoid bone, and one to the skull base. Three of the patients were staged T3, and seven T4. Two patients had lymph nodes metastases at their initial presentation, and were staged T4. All of the cases were histopathologically confirmed.
CONCLUSION: The accurate analysis of the tumor local extent and dissemination by means of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging plays a relevant role in the surgical planning, besides influencing the therapeutic conduct and prognosis.
Keywords: Squamous cell carcinoma; X-ray tomography; Cancer; Maxillary sinus.
INTRODUCTION
Maxillary sinus carcinomas are rare, comprising 0.20.8% of neoplasms, 3% of head and neck carcinomas, and 80% of all cases of paranasal sinus tumors(1,2).
The majority of tumors occurring in the maxillary antrum are of epithelial origin and epidermoid carcinomas correspond to more than 80% of all cases of malignant neoplasms, the adenocystic carcinoma being the second more frequent of them(2).
The majority of patients present with an advanced stage of the disease at the first symptoms presentation(2).
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are well-established and useful techniques for evaluating the tumor extension to adjacent areas.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The authors performed a retrospective analysis of ten cases of maxillary sinus carcinomas diagnosed and treated by Services of Diagnostic Imaging and Head and Neck Surgery at Hospital Heliópolis, São Paulo, SP, in the period between 1988 and 2002 (Table 1).
Seven (70%) patients had epidermoid histological type tumors, and three (30%), adenocystic type. Six (60%) patients were men and four (40%) women. With ages ranging between 37 and 77 years (mean age = 61 years). Seven (70%) patients had a history of tobacco use, and four (40%) alcohol. At the patients' presentation, main symptoms were: pain and edema in the pre-maxillary region (70%), nasal obstruction (20%) and dental pain (30%). All of them underwent CT scan, and two, also MRI. Axial and coronal CT images acquisition was performed with the gantry parallel to the infraorbitomeatal line, 5 mm slice thickness and increment, following intravenous iodine contrast injection.
Nine (90%) patients had not undergone any treatment before the examination and one (10%) had been submitted to surgery and radiotherapy. The images were evaluated as to tumor site of origin, extent and lymph node involvement, by a 15-year head-and-neck experience Doctor in Radiology. The staging was based on a combination of physical examination with radiological study (CT), and the tumors were classified according to International Union Against Cancer (UICC, 1997), into:
T1 Tumor confined to the infrastructure antral mucosa, without bony erosion.
T2 Tumor confined to the suprastructure antral mucosa, without bony erosion, or to the infrastructure, with inferior or medial bony wall destruction.
T3 Tumor invading any of the following sites: genal skin, orbit, cribriform plate, anterior ethmoid bone or pterygoid musculature.
T4 Tumor invading the cribriform plate, posterior ethmoid bone, pterygoid plates or the skull base.
RESULTS
Nine patients (90%) presented tumor extension to the cheek, eight (80%) to the masticator space, eight to the maxillary sinus floor and hard palate (80%), seven to the nasal cavity (70%), five to the pterygoid fossa (50%), five to the orbit (50%), three to the ethmoid bone (30%), and one to the skull base (10%). Three patients (30%) were staged as T3, and seven (70%) as T4, none as T1 and T2. Two (20%) patients had T4 lymph node metastasis at their initial presentation. The diagnosis of lymphadenopathy was based on physical examination, imaging and cytological studies. Three (30%) patients were submitted only to surgery; four (40%), to surgery and radiotherapy; one (10%), to chemotherapy and one (10%), to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Correlation with surgical findings has been feasible in seven patients (70%). All of the cases were confirmed by means of biopsy and histopathological study.
DISCUSSION
Approximately 85% of antromaxillary neoplasms are epidermoid carcinomas, and 5% to 15% adenocystic(3).
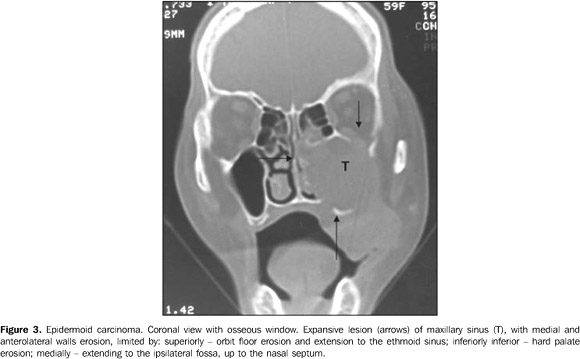
Because of the tumor localization and absence of early symptoms, the patients usually present with advanced tumors at the moment of diagnosis(2), and, when the tumors are small sized, they are misdiagnosed as chronic sinusitis, nasal polyp, lacrimal duct obstruction, or even cranial arteritis(2). In 40% to 60% of cases there are facial asymmetry, oral cavity swelling and tumor extension to the nasal cavity. These lesions extend medially towards the nasal cavity; superiorly they may invade the orbit and ethmoid sinus; anterolaterally, they may reach soft tissues and cheek; and, inferiorly, the maxillary sinus floor, dental alveolus and palate. Posteriorly, they may reach the pterygopalatine fossa and pterygoid muscles. Through the pterygoid fossa, they may superiorly extend towards the orbital fissure and the cavernous sinus(2). All of the ten patients presented with one or more of these extensions.
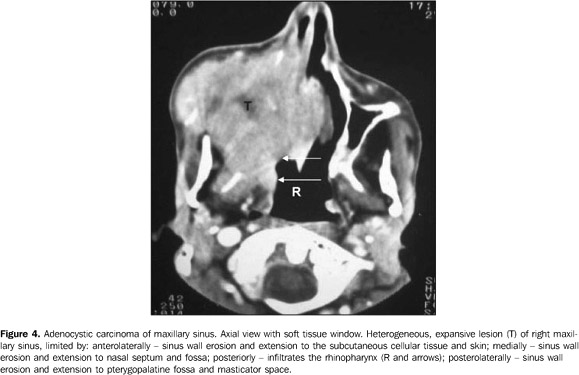
Adenocystic carcinomas of the maxillary antrum seem to present a more aggressive behavior than those of the salivary glands. Invasion into facial and orbital bones is relatively frequent and affects the skull base. Also, they may reach the meninges and latter the brain; however, generally, there is little or no bone architecture alteration at radiological studies. Another way of spread is by perineural invasion, the maxillary, mandibular and pterygoid nerves, respectively through the round, oval foramens, and pterygoid canal, being the vectors(4). Two (66.6%) of the three patients with adenocystic carcinoma presented intracranial extension by the tumor.
Lymph node blocks on the neck as an initial presentation are not frequent, appearing in 3% to 20% of cases(5). This low incidence may be associated with the poor lymphatic draining of the maxillary sinus, or with the clinical inaccessibility for the affected lymph nodes diagnosis(6). The topographic distribution of lymph node metastasis in the neck usually is dependent on the tumor site, contiguity and high number of capillaries(7). Patients with tumor extension to the nasopharynx and oral cavity present a higher incidence of cervical metastases than in other regions(8). In the present study, two (20%) patients had metastases to the upper jugulo-carotid chain, and extension to the oral cavity. St. Pierre and Baker have emphasized the worst prognosis when associated with lymph node metastasis(9).
Distant metastasis incidence usually is low in cases of epidermoid carcinoma of the maxillary sinus(10), and is more frequent in the poorly differentiated subtype. Frequently, adenocystic carcinoma distant metastases occur tardively(4). Lungs and bones are the sites most frequently affected(11). In our sample, two patients (20%) one with epidermoid carcinoma (14,2%) and another with adenocystic carcinoma (33,3%) presented hematogenous metastasis to the lungs, respectively six an ten months following the surgery.
The primary reason for ordering CT and MRI studies in cases of maxillary sinus carcinoma, is for better characterizing the invasion of structures beyond the site of origin(2). On CT studies all of the cases present as soft tissue masses in the maxillary sinus cavity, with 70% to 90% of cases evidencing bony destruction(2). CT provides more details of bone involvement than MRI(12). At MRI, these tumors present middle signal intensity on T1-weighted images and high intensity signal on T2-weighted images, and this method is of help in the evaluation of the posterior cranial fossa, orbit, and perineural/perivascular dissemination, besides allowing the differentiation between retained secretions and neoplastic tissue(12). Usually, CT and MRI may be complementary in the staging of paranasal sinus tumors, according to Loevner & Sonners(13). The most effective barrier against tumors propagation is the integrity of the periosteum that is particularly more resistant in two critical areas: the skull base and orbit(14).
The surgery/postsurgical radiotherapy combination results in survival rates higher than those for radiotherapy alone. Tumors causing skull base destruction or involving the internal carotid artery are irresectable. In these cases, even with combined surgery and post-surgical radiotherapy, they do not present a good prognosis, so this method is preferable for patients who have developed distant metastases(10). Radiotherapy is accepted as a palliative method in inoperable cases. Some authors have recommended an aggressive treatment for patients with metastatic disease(15).
The poor prognosis of maxillary sinus carcinoma may be due to the delayed detection of extensive tumors and the impossibility of a complete surgical. The five-year survival rate ranges between 20% and 40%(2,16). Ohngren has divided the maxillary antrum into posterosuperior and anteroinferior segments, drawing a line from the mandible angle on the profile face image, and has suggested that a tumor confined to the anteroinferior portion could present a better prognosis(2). Patients with perineural invasion had an unfavorable prognosis(17). According to the dossiers review, the majority of patients had advanced disease at the moment of admission into the hospital.
CONCLUSION
The accurate analysis of the tumor local extent and dissemination allowed by CT and MRI plays a significant role in the surgical planning, also influencing the therapeutic conduct and prognosis.
REFERENCES
Received March 8, 2004.
Accepted after revision January 27, 2005.
- 1. Le QT, Fu KK, Kaplan M, Terris DJ, Fee WE, Goffinet DR. Treatment of maxillary sinus carcinoma: a comparison of the 1997 and 1977 American Joint Committee on cancer staging systems. Cancer 1999;86:17001711.
- 2. Som PM, Brandwein M. Sinonasal cavities. Inflammatory diseases, tumours, fractures and postoperative findings. In: Som PM, Hugh D, editors. Head and neck imaging. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book, 1996.
- 3. Lavertu P, Roberts JK, Kraus DH, et al Squamous cell carcinoma of the paranasal sinuses: the Cleveland Clinic experience 19771986. Laryngoscope 1989;99:11301136.
- 4. Kim GE, Park HC, Keum KC, et al Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the maxillary antrum. Am J Otolaryngol 1999;20:7784.
- 5. Stern SJ, Hanna E. Cancer of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. In: Meyer EN, Suen JY, editors. Cancer of the head and neck. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1996;205233.
- 6. Shibuya H, Yasumoto N, Gomi N, Yamada I, Ohashi I, Suzuki S. CT features in second cancers of the maxillary sinus. Acta Radiol 1991;32: 105109.
- 7. Donald PJ. Intranasal and paranasal sinus carcinoma. In: Thawley SE, Pange WR, editors. Comprehensive management of the head and neck tumors. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1987.
- 8. Kim GE, Chung EJ, Lim JJ, et al Clinical significance of neck node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary antrum. Am J Otolaryngol 1999;20:383390.
- 9. St. Pierre S, Baker SR. Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus: analysis of 66 cases. Head Neck Surg 1983;5:508513.
- 10. Konno A, Ishikawa K, Terada N, Numata T, Nagata H, Okamoto Y. Analysis of long-term results of our combination therapy for squamous cell cancer of the maxillary sinus. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 1998;537:5766.
- 11. Matsuba HM, Thawley SE, Simpson JR, Levine LA, Mauney M. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of major and minor salivary gland origin. Laryngoscope 1984;94:13161318.
- 12. Maroldi R, Farina D, Battaglia G, Maculotti P, Nicolai P, Chiesa A. MR of malignant nasosinusal neoplasms. Frequently asked questions. Eur J Radiol 1997;24:181190.
- 13. Loevner LA, Sonners AI. Imaging of neoplasms of the paranasal sinuses. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2002;10:467493.
- 14. Kimmelman CP, Korovin GS. Management of paranasal sinus neoplasms invading the orbit. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1988;21:7792.
- 15. Howard DJ, Lund VJ. Reflections on the management of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1985;93:338341.
- 16. Leafstedt SW, Gaeta JF, Sako K, Marchetta F, Shed DP. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the major and minor salivary glands. Am J Surg 1971;122: 756762.
- 17. Matsumoto S, Shibuya H, Tatera S, Yamazaki E, Suzuki S. Comparison of CT findings in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus. Acta Radiol 1992; 33:523527.
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
07 Feb 2007 -
Date of issue
Dec 2006
History
-
Accepted
27 Jan 2005 -
Received
08 Mar 2004