ABSTRACT
Guava (Psidium guajava) can be parasitized by the plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne enterolobii, which causes a complex disease. Research on resistance involves studying infection, nematode multiplication in roots, and early symptom expression. This study aimed to confirm Meloidogyne enterolobii resistance in Psidium genotypes selected as potential guava rootstocks after their clonal propagation and determine the symptomatology associated with plant infection by evaluating leaf pigmentation indices and seedling growth rates. The experiment was conducted in a protected environment at the Research Support Unit of the State University of Northern Rio de Janeiro, in Campos dos Goytacazes, Rio de Janeiro state (RJ), between August 2023 and March 2024. A randomized block design was used, with seven treatments, 12 replicates, and one plant per plot. Seedlings, obtained through mini-cutting, were inoculated with 2,000 eggs and second-stage juveniles (J2) of M. enterolobii, and evaluated over 135 days. The resistance levels previously identified in seed-propagated seedlings were not consistently confirmed after vegetative propagation. Early parasitism symptoms coincided with changes in leaf pigment indices. The susceptibility of most genotypes, previously classified as resistant, suggests that epigenetic factors may influence the expression of resistance to M. enterolobii.
Key words:
root-knot nematode; rootstock; Psidium cattleianum; Psidium guajava; vegetative propagation
HIGHLIGHTS:
Propagation method and physiological conditions affect Psidium resistance to nematodes.
Leaf pigment indices are early indicators of nematode stress.
Chlorophyll and nitrogen balance index decline with increased nematode multiplication in the root environment.

 Changes in root environment affect Meloidogyne enterolobii resistance and pigment synthesis in Psidium
Changes in root environment affect Meloidogyne enterolobii resistance and pigment synthesis in Psidium
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
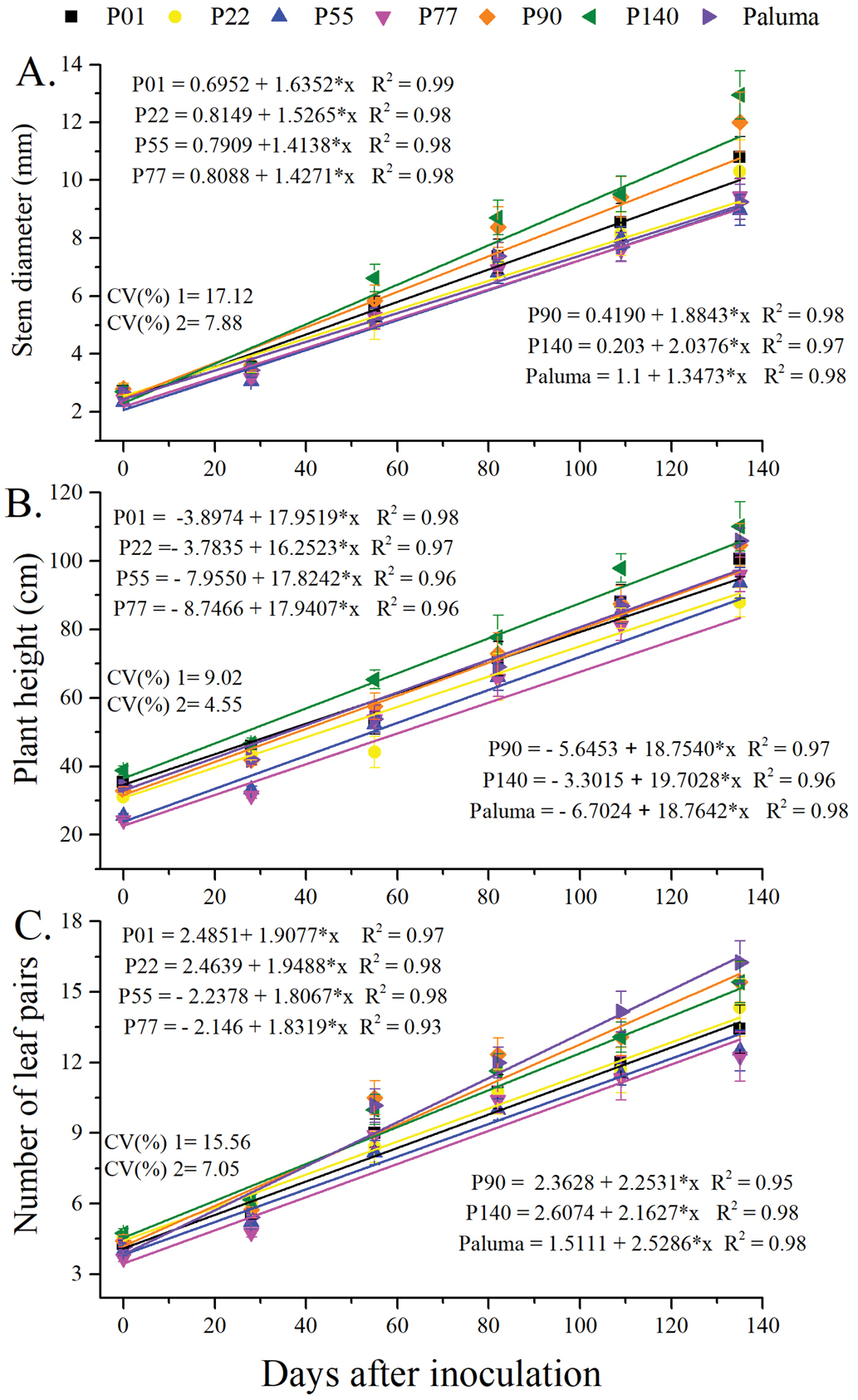 The vertical bars represent the standard error (n = x); * p ≤ 0.05 (F test); CV1 - Coefficient of variation among genotypes (main factor). CV2 - Coefficient of variation within time (subplots)
The vertical bars represent the standard error (n = x); * p ≤ 0.05 (F test); CV1 - Coefficient of variation among genotypes (main factor). CV2 - Coefficient of variation within time (subplots)
 The vertical bars represent the standard error (n = x); * p ≤ 0.05 (F test); CV1 - Coefficient of variation among genotypes (main factor). CV2 - Coefficient of variation within time (subplots).
The vertical bars represent the standard error (n = x); * p ≤ 0.05 (F test); CV1 - Coefficient of variation among genotypes (main factor). CV2 - Coefficient of variation within time (subplots).
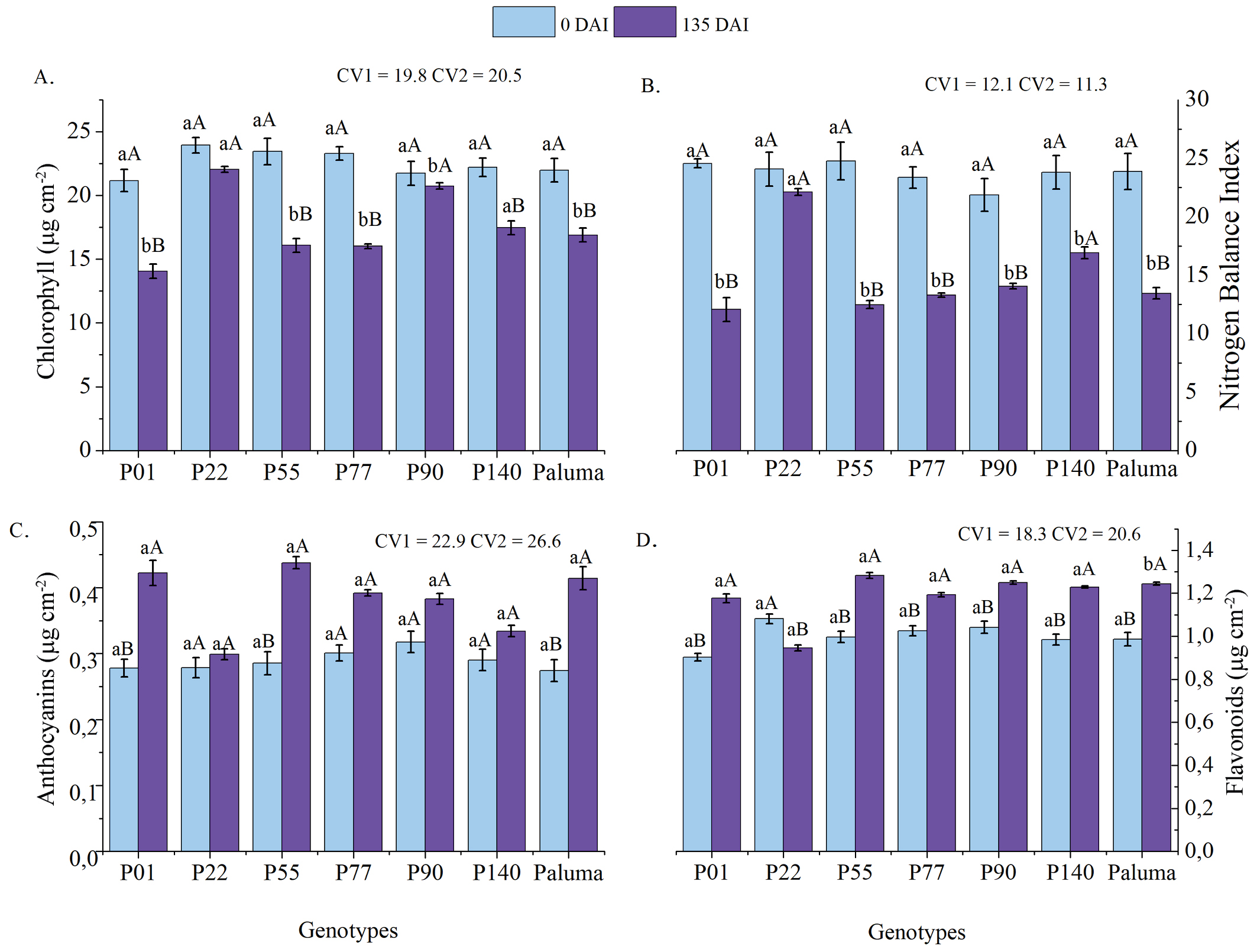 The vertical bars represent the standard error (n = x); Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between genotypes at each time point, while different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between time points for the same genotype, according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05); CV1 - Coefficient of variation among genotypes (main factor). CV2 - Coefficient of variation within time (subplots). DAI - days after inoculation
The vertical bars represent the standard error (n = x); Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between genotypes at each time point, while different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between time points for the same genotype, according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05); CV1 - Coefficient of variation among genotypes (main factor). CV2 - Coefficient of variation within time (subplots). DAI - days after inoculation
 RFM - Root fresh mass, CHL - Chlorophyll, NBI - Nitrogen balance index, FP - Final population, RF - Reproduction factor
RFM - Root fresh mass, CHL - Chlorophyll, NBI - Nitrogen balance index, FP - Final population, RF - Reproduction factor