ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The respiratory compensation point (RCP) is the metabolic rate for a maximal incremental test, from which the control of the acid-base balance is lost. However, the critical velocity (CV) defines the upper limit of the heavy exercise domain, in which the exhaustion is not related to metabolic disturbance.
Objective:
To compare the physiological (heart rate - HR, blood lactate - [La], and oxygen uptake - V̇O2) and perceptual (rating of perceived exertion - RPE) responses, while exercising at CV and at RCP, in order to analyze contextual similarities.
Methods:
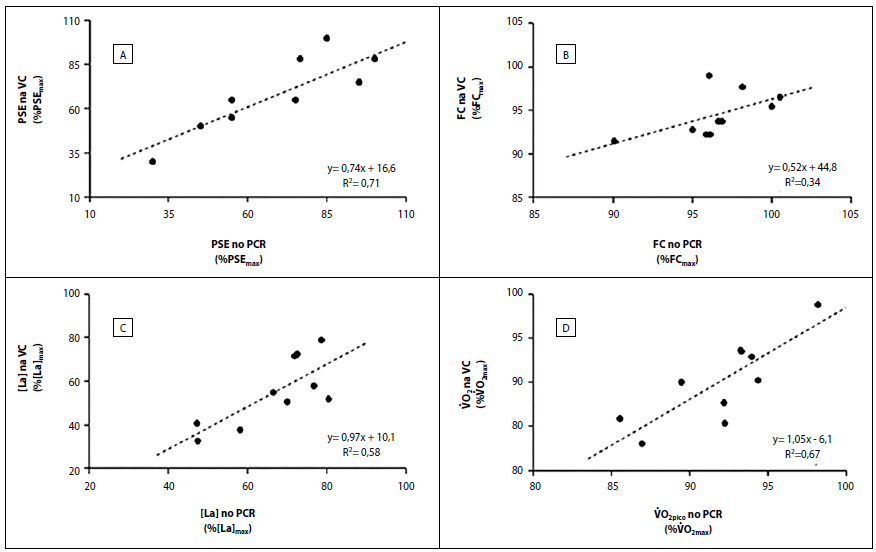
Ten adolescent runners (15.8±1.7 years old) underwent progressive test (increments of 1.0 km×h-1 per minute until exhaustion) to determine V̇O2max, RCP and the correspondent velocities. The CV was estimated for three efforts with time limit of 2 to 12 minutes. The participants performed two efforts of seven minutes each on separate days, in CV and vRCP HR, RPE (scale 6-20) were recorded every minute, and [La] was measured at rest and after each effort. The V̇O2 was analyzed breath by breath during efforts. The Mann-Whitney test compared HR, [La], V̇O2, and RPE responses in CV and vRCP. The variance between these responses was examined by the scatter coefficient (R2). The significance level was P≤0.05.
Results:
The maximum values in the progressive test were 56.1±5.5 ml×kg-1×min-1 (V̇O2max), 16.5±1.7 km×h-1 (vV̇O2max), 202±12 bpm (HRmax), 19.4±1.3 (RPE) and 12.7±3.1 mmol×L-1 ([La]). No differences were observed between CV (at 83.8±3.6% vV̇O2max) and vRCP (at 86.5±3.6% vV̇O2max) in RPE responses (P=0.761), HR (P=0.096), [La] (P=0.104) and V̇O2 (P=0.364) responses. Correlations were observed between the CV and vRCP in [La] (R2=0.76; P=0.011), RPE (R2=0.84; P<0.01) and V̇O2max (R2=0.82; P<0.01) responses.
Conclusion:
It was inferred that exercise in RCP reproduced a physiological and perceptual response similar to that in CV.
Keywords:
oxygen consumption; heart rate; lactic acid; exercise