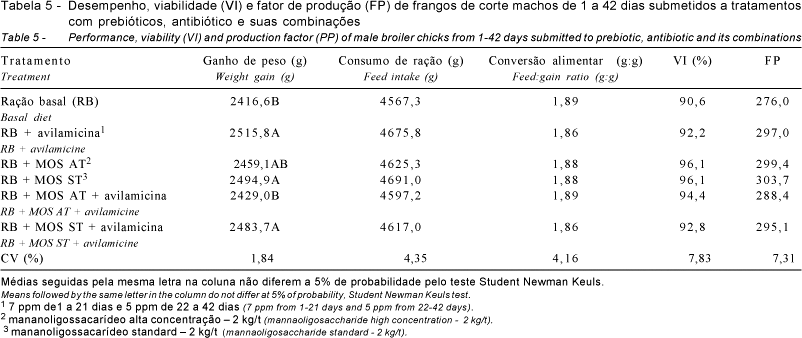
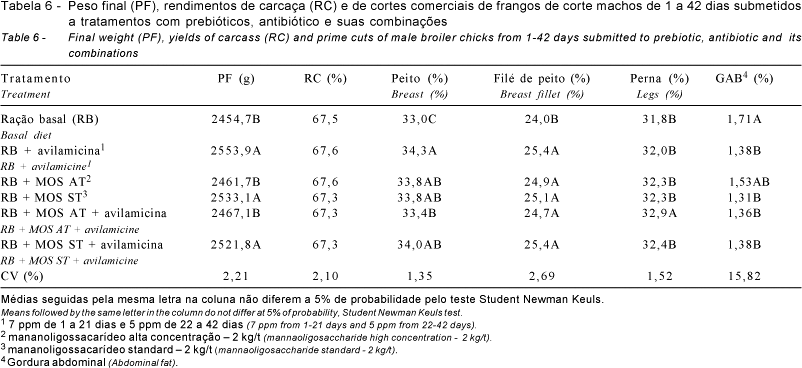
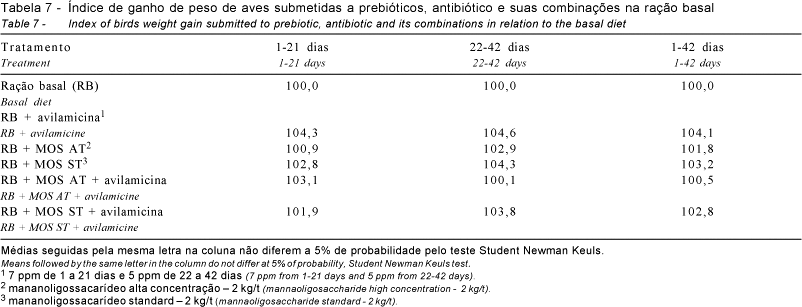
This trial was conducted to study the use of mannanoligosaccharide (standard and concentrate) on chicks diets. One thousand and eigthy 1-d male chicks (Ross) averaging 42 g of initial BW were assigned to a completely randomized experiment with nine replications of 20 birds per experimental unit. The following treatments were analyzed: control, antibiotic (avilamicine), mannaoligosaccharide high concentration (MOS AT), mannaoligosaccharide standard (MOS ST), MOS AT + antibiotic, and MOS ST + antibiotic. The birds were reared in wood powder, reused of a lot previously housed. Weight gain, feed intake, feed:gain ratio, viability and prime cuts yield were evaluated. In the period from 1 to 21 days old, no significant differences across the treatments on feed intake, feed:gain ratio, and viability were found. The results of performance of birds fed diet containing MOS ST or MOS AT combined or not with the antibiotic, did not differ form those of treatments with avilamicin and control. In the period from 1 to 42 days old, mannanoligosaccharides standard (MOS ST) combined or not with avilamicin, increased weight gain, whereas the mannaoligosaccharide high concentration (MOS AT) showed did not affect weight gain. Feed:gain ratio, feed intake and viability were not affected by the different treatments, but the additives increased prime cuts yield and it decreased abdominal fat.
additive; antibiotic; feed efficiency; MOS