Abstracts
Purpose
to characterize and to compare the hearing of employees of a public hospital exposed to maximum occupational noise levels above and below 85dB(A).
Methods
this clinical study selected 39 workers of a public hospital, divided according to the level of noise exposure: 20 subjects with maximum exposure levels above 85dB(A) (Group 1) and 19 individuals with maximum exposure levels below 85dB(A) (Group 2). Basic audiological evaluation, transient and distortion product otoacoustic emissions were carried out.
Results
both groups presented normal hearing thresholds. However, 87.5% in Group 1 and 60.5% in Group 2 showed absent responses in transient evoked otoacoustic emissions, with statistical difference. Group 2 showed higher signal/noise ratios also in distortion product otoacoustic emissions, and only the frequency of 6 kHz was abnormal in both groups.
Conclusion
sound pressure levels and noise exposure time did not influence in pure tone thresholds. The higher the sound pressure level and the longer the exposure time, more altered the otoacoustic emissions, indicating cochlear dysfunction.
Noise; Occupational; Hearing; Hearing Loss; Noise-Induced; Audiometry; Otoacoustic Emissions; Spontaneous
Objetivo
caracterizar e comparar a audição de funcionários de um hospital público expostos a níveis de ruído ocupacional máximos superiores e inferiores a 85dB(A).
Métodos
trata-se de um estudo clínico, com 39 funcionários de um hospital público, divididos de acordo com o nível de exposição ao ruído: 20 indivíduos sob exposição máxima superior a 85dB(A) (Grupo 1) e 19 indivíduos sob exposição máxima inferior a 85dB(A) (Grupo 2). Foi realizada avaliação audiológica básica e emissões otoacústicas evocadas por estímulo transiente e produto de distorção.
Resultados
ambos os grupos apresentaram limiares de audibilidade normais. Contudo, observou-se ausência de respostas em 87,5% no Grupo 1 e 60,5% no Grupo 2 no teste de emissões otoacústicas evocadas por estímulo transiente, com diferença estatística. O Grupo 1 mostrou menor amplitude de respostas também às emissões otoacústicas produto de distorção, sendo a frequência de 6kHz a única alterada em ambos os grupos.
Conclusão
os níveis de pressão sonora e o tempo de exposição não influenciam os limiares auditivos tonais. As emissões otoacústicas mostraram-se mais alteradas quanto maior o nível de pressão sonora e tempo de exposição.
Ruído Ocupacional; Audição; Perda Auditiva Provocada por Ruído; Audiometria; Emissões Otoacústicas Espontâneas
INTRODUCTION
Among the several occupational risk elements, noise is, indeed, the most common physical agent and the one that causes the worst effect onto hearing in the work environment.
Noise is defined as an unpleasant hearing sensation, arisen from a series of
inharmonic frequencies, which stem from the most diverse sources11 . Fernandes M, Morata TC. Estudo dos efeitos auditivos e
extra-auditivos da exposição ocupacional a ruído e vibração. Rev Bras
Otorrinolaringol. [periódico na internet]. 2002 Oct [cited 2011 Dec
22];68(5):705-13. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992002000500017&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992002000500017.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
.
Environmental sound pollution, one of the consequences of the modern world, has
currently become so ubiquitous that places free of excessive noise are very
rarely found. Even in hospitals, where the environment should be silent, levels
of potentially damaging noise are ever-present, resulting from the technological
advances and from lack of guidance to the hospital teams, a situation that
generates an incessant concern in the area of public health22 . Pereira RP, Toledo RN, Amaral JLG, Guilherme A. Qualificação e
quantificação da exposição sonora ambiental em uma unidade de terapia intensiva
geral. Rev. Bras. Otorrinolaringol. [periódico na internet] 2003 [citado 2011
Dez 22];69(6):766-71. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992003000600007&lng=pt.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992003000600007.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
.
Numberless studies have indicated the extreme noise in several hospital
environments, and pointed out the need for prevention, as well as, for proper
guidance for the professionals, particularly regarding those involved with the
area of health, where, theoretically, the awareness for silence should be of
major importance22 . Pereira RP, Toledo RN, Amaral JLG, Guilherme A. Qualificação e
quantificação da exposição sonora ambiental em uma unidade de terapia intensiva
geral. Rev. Bras. Otorrinolaringol. [periódico na internet] 2003 [citado 2011
Dez 22];69(6):766-71. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992003000600007&lng=pt.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992003000600007.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
3 . Rodarte MDO, Scochi CGS, Leite AM, Fujinaga CI, Zamberlan NE,
Castral TC. O ruído gerado durante a manipulação das incubadoras: implicações
para o cuidado de enfermagem. Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem.
2005;13(1):79-85.
4 . Achutan C. Assessment of noise exposure in a hospital kitchen.
Noise Health. 2009;11(44):145-50.
5 . Otenio MH, Cremer E, Claro EMT. Intensidade de ruído em hospital
de 222 leitos na 18ª Regional de Saúde - PR. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico
na internet] 2007 Apr [cited 2011 Dec 22];73(2):245-50. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992007000200016&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992007000200016.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
6 . Macedo ISC, Mateus DC, Costa EMGC, Asprino ACL, Lourenço EA.
Avaliação do ruído em Unidades de Terapia Intensiva. Braz. J Otorhinolaryngol.
[periódico na internet]. 2009 [cited 2011 Dec 22]; 75(6):844-6. Disponível em:
URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1808-86942009000600012&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1808-86942009000600012.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
-77 . Silva MC, Orlandi CG, Chang EM, Siviero J, Pinto MM, Armellini PFS
et al . Níveis de ruído na lavanderia de um hospital público. Rev. CEFAC.
2011;13(3):472-8..
In a previous study, performed in the same hospital, the noise level in the laundry areas was appraised (variation of noise level from 82 to 95dB); in the maintenance sector (variation of noise level ranged from 61 to 113 dB), nutrition area (variation of noise level from 73 to 89dB) and in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit – NICU of a public hospital (variation of noise level ranged from 50 to 74 dB); it was also realized that, exception made to the NICU, all the other sectors showed minimum and maximum levels of intermittent noise, surpassing the levels established in the legislation concerning hospital environments88 . Silva MC. Níveis de ruído no ambiente hospitalar: impacto na qualidade de vida [dissertação]. São Paulo (SP): Universidade Federal de São Paulo; 2009..
The long-lasting exposure to high levels of sound pressure can cause a continued
lessening of the hearing capacity, known as Hearing Loss Induced by Noise
(HLIN). Ordinarily related to occupational noise, HLIN’s main features are its
being a type of neurosensory, irreversible, often bilateral and progressive, in
case the exposure is not discontinued. Nevertheless, in many cases, the hearing
alteration is not readily evidenced in the audiometry. Several studies have
recognized that even the individuals exposed to occupational noise within the
normal hearing threshold, revealed alterations in the register of otoacoustic
emissions, both through transient stimuli and the product distortion, evidencing
the relevance of such tests for the HLIN precocious diagnosis99 . Leme OLS. Estudo audiométrico comparativo entre trabalhadores de
área hospitalar expostos e não expostos a ruído. Rev. Bras. Otorrinolaringol
[periódico na internet]. 2001 [citado 2011 Dez 22];67(6):837-43. Disponível em:
URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992001000600013&lng=pt.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992001000600013.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
10 . Balatsouras DG. The evaluation of noise-induced hearing loss with
distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Med Sci Monit. [periódico na
internet]. 2004 May [citado 2011 Dez 22];10(5):CR218-22. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?ICID=11654.
http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?I...
11 . Marques FP, Costa EA. Exposição ao ruído ocupacional: alterações
no exame de emissões otoacústicas. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico na
internet]. 2006 [cited 2011 Dec 22];72(3):362-6. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992006000300011&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992006000300011.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
12 . Job A, Raynal M, Kossowski M, Studler M, Ghernaouti C,
Baffioni-Venturi A et al. Otoacoustic detection of risk of early hearing loss in
ears with normal audiograms: a 3-year follow-up study. Hear Res.
2009;251(1-2):10-6.-1313 . Coelho MSB, Ferraz JRS, Almeida EOC, Almeida FN. As emissões
otoacústicas no diagnóstico diferencial das perdas auditivas induzidas por
ruído. Rev. CEFAC [periódico na internet]. 2010 [cited 2011 Dec
22];12(6):1050-8. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-18462010000600017&lng=en.
Epub Nov 19, 2010.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-18462010005000108.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
.
Frequently associated to buzzing, the hearing loss can also unveil other hearing
symptoms, such as hypoacusia, vertigo 1414 . Ogido R, Costa EA, Machado HC. Prevalência de sintomas auditivos e
vestibulares em trabalhadores expostos a ruído ocupacional. Rev. Saúde Pública
[periódico na internet]. 2009 [cited 2011 Dec 22];43(2):377-80. Disponível em:
URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-89102009000200021&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89102009000200021.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
, recruitment, besides other extra-hearing
ailments, such cephalalgia, insomnia, stress, poor concentration, among
others55 . Otenio MH, Cremer E, Claro EMT. Intensidade de ruído em hospital
de 222 leitos na 18ª Regional de Saúde - PR. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico
na internet] 2007 Apr [cited 2011 Dec 22];73(2):245-50. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992007000200016&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992007000200016.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
.
Together, such stress features increase the risk of accidents at work and may
eventually give rise to multiple effects to the workers’ health and
wellbeing11 . Fernandes M, Morata TC. Estudo dos efeitos auditivos e
extra-auditivos da exposição ocupacional a ruído e vibração. Rev Bras
Otorrinolaringol. [periódico na internet]. 2002 Oct [cited 2011 Dec
22];68(5):705-13. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992002000500017&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992002000500017.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
.
Due to the foregoing, the objectives of this study were: to describe and compare the tonal threshold and the otoacoustic emissions evoked by transient stimuli and distortion product of workers exposed to noise in a public hospital.
METHODS
This transversal-descriptive-type study, was approved by the Ethics Committee in Research Universidade Federal de São Paulo, under the register number 1867/09.
The sample involved 39 randomly-selected employees of a hospital, being 10 of them from the laundry sector (variation of noise level ranging from 82 to 95 dB), 10 individuals of the maintenance sector (comprehending the carpentry and metalworking sectors, with noise level from 61 to 113 dB), 10 individuals of the nutrition area (variation of noise level ranging from 73 to 89 dB) and 5 individuals from the NICU (variation of noise level ranging from 50 to 74 dB).
The variables regarding sex, age and occupation were not taken into consideration for the selection of volunteers. The inclusion comprised only employees who had been exposed to occupational noise for at least 2 years and who presented a type A tympanometric, which indicates integrity of the middle ear; the ones who suffered from prior hearing deficiency with defined etiology were excluded.
All the workers were exposed to intense continuous or intermittent noise for, at least, eight hours per day (graphics and maintenance sectors) or in the system of 12 x 24 hours (sectors of nutrition, laundry and NICU).
The adopted criterion for the division into groups was the maximum level of exposure to which the employees were submitted to. Thus, two groups were formed, to wit: Group 1- Higher Exposure -comprised of 20 individuals under maximum exposure level of noise higher than 85 dB (A), comprehending the sectors of laundry and maintenance; and Group 2- Lower Exposure – formed by 19 individuals, under maximum exposure level of noise lower than 85 dB (B), comprehending the sectors of nutrition, graphics and NICU.
Each volunteer was scheduled for an individual date for audiological tests, performed in a single session in the Audiology Clinic, which lasted about one hour, subsequent to hearing-free rest of at least 14 hours.
On the appointed date for the evaluation, a clinical-occupational-anamnesis was carried out with each participant, who had previously signed an Instrument of Free Clear Consent.
After the anamnesis, the individuals were submitted to audiological evaluation comprised of the procedures that follow: meatoscopy, tonal liminal audiometry (from 250 Hz to 8000Hz) through the descending-ascending technique and vocal audiometry (LRF and IPRF), having both procedures made use of the MA41 audiometer, inside an acoustic cabin with environmental noise isolation; measurements of acoustic immitance as a means of evaluating the conditions of the middle ear; otoacoustic emissions evoked by transient stimuli (TEOAE [otoacoustic emissions] ) and by a product of distortion (DPOAE[otoacoustic emissions- product distortion] ), obtained in the equipment ILO 92.
Audibility threshold equal to or lower than 25 dBNA were deemed normal. As for the TEOAE analysis, the general response for the qualitative testing and the presence of response higher than 3dB in the frequency bands 2, 3 and 4 kHz for the quantitative analysis were taken into account.
So as to classify the presence of DPOAE, the response should be equal to or higher than 6dB in the frequencies from 1 to 6kHz1515 . Durante AS. Emissões Otoacústicas. In: Bevilacqua MC, Martinez MAN, Balen AS, Pupo AC, Reis ACM, Frota S. Tratado de Audiologia. São Paulo: Santos; 2011. p. 145-58..
The statistic treatment of the set of data aimed at analyzing and comparing the hearing threshold and the TEOAE’s and DPOAE’s quantitative and qualitative responses in both groups, besides studying the hearing habits of such population. Tests were applied: parametric test ANOVA -– Analysis of Variance, the Mann-Whitney test of Equality of Two Proportions, with significance level of 5% and 95% statistic reliance33 . Rodarte MDO, Scochi CGS, Leite AM, Fujinaga CI, Zamberlan NE, Castral TC. O ruído gerado durante a manipulação das incubadoras: implicações para o cuidado de enfermagem. Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem. 2005;13(1):79-85..
RESULTS
Concerning the studied groups, it was clear that the average work period with exposure to previous noise up to the research date was higher for Group 1, 20 years of exposure against 12,2 years of exposure of Group 2. No statistically significant differences were found between the right ears and the left ears, proving that there had been no effect of the side of the tested ear in any of the performed audiological tests. Thus, in the audiological tests analyses, both ears were evaluated.
Figure 1 shows the comparison of the audibility threshold in Groups 1 and Group 2, wherefrom it was evidenced that both groups presented average of audibility threshold within the standards of normality for all the tested frequencies. There was a statistically significant difference between the groups only for the frequencies of 1000Hz (p-value=0.002) and 4000Hz (p-value = 0.036), with lower thresholds in Group 1 when compared to Group 2.
The TEOAE analysis showed a statistic difference between the groups, with 87.5% of absence of responses in Group 1, against 60.5% in Group 2 (Table 1).
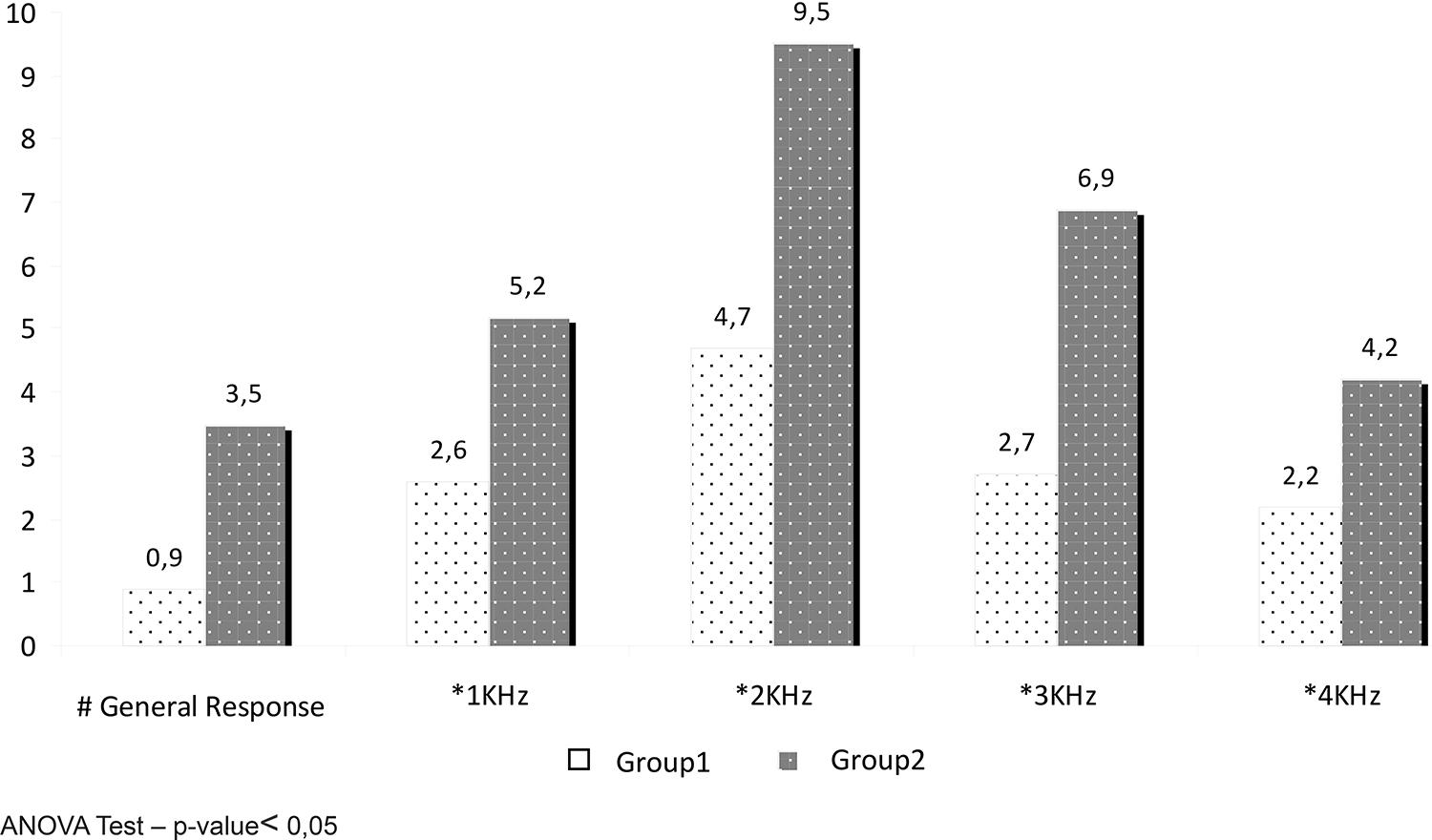
As regards the quantitative results, a statistically significant difference was realized for bands of frequency 1000Hz (p-value=0.044), 2000Hz (p-value=0.002), and 3000Hz (p-value=0.001) in the groups, with greater amplitude of responses in Group 2 in relation to Group 1. (Figure 2). The General Response displayed a tendency to the statistical significance (p-value=0.059), with greater amplitude of responses in Group 2, as well.
Descriptive measurements of the General Response and band frequencies of 1, 2, 3 and 4kHZ of the TEOAE test for Group1 and Group 2
When comparing the average amplitude of Groups 1 and 2 in the DPOAE, there was a statistically significant difference in frequencies from 2 to 5kHz (p-value=0.018 and 0.050, respectively), with greater amplitude of responses in Group 2 in both frequencies. Besides, it was pointed out that the 6kHz frequency presented altered values in both groups (Figure 3).
Descriptive measurements of frequencies of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6kHZ of the DPOAEtest for Group1 and Group 2 (in dB)
DISCUSSION
In the present study, both Group 1 and Group 2 presented average tonal hearing
threshold within the standards of normality for all the tested frequencies
(Figure 1). Other studies showed a hearing loss in different levels in most of
the individuals exposed to noise and who were submitted to tonal audiometry
99 . Leme OLS. Estudo audiométrico comparativo entre trabalhadores de
área hospitalar expostos e não expostos a ruído. Rev. Bras. Otorrinolaringol
[periódico na internet]. 2001 [citado 2011 Dez 22];67(6):837-43. Disponível em:
URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992001000600013&lng=pt.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992001000600013.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
,1616 . Almeida SIC, Albernaz PLM, Zaia PA, Xavier OG, Karazawa EHI.
História natural da perda auditiva ocupacional provocada por ruído. Rev. Assoc.
Med. Bras. [periódico na internet]. 2000 [cited 2012-05-08];46(2):143-58.
Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-42302000000200009&lng=en&nrm=iso.
ISSN 0104-4230.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0104-42302000000200009.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
,1717 . Dias A, Cordeiro A, Corrente JE, Gonçalves CGO. Associação entre
perda auditiva induzida pelo ruído e zumbidos. Cad. Saúde Pública [periódico na
internet]. 2006 [cited 2011 Dec 22];22(1):63-8. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102-311X2006000100007&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2006000100007.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
, which differs from the
results found in this research. A justification for such a finding would be the
noise level to which this study’s participants have been exposed to, that is,
maximum levels lower or higher than 85dB (A). It is well known that the risk for
PAIR occurrence happens more often under exposure levels higher than 85dB
(A)88 . Silva MC. Níveis de ruído no ambiente hospitalar: impacto na
qualidade de vida [dissertação]. São Paulo (SP): Universidade Federal de São
Paulo; 2009..
Nevertheless, there was a statistically significant difference for the frequencies of 1 and 4 kHz, with the worst threshold in Group 1, when compared to Group 2. Even though there was not a statistically significant difference in the comparison between the groups, the 6kHz frequency showed higher threshold in both groups, when compared to all the other tested frequencies.
According to the National Committee of Noise and Auditive Preservation 1919 . Comitê Nacional de Ruído e Conservação Auditiva. Perda auditiva induzida por ruído relacionada ao trabalho. Boletim, São Paulo, n. 1, 29 jun. 1994. Revisto em 14 nov. 1999., one of the symptoms of hearing loss induced by noise, is the beginning and the predominance44 . Achutan C. Assessment of noise exposure in a hospital kitchen. Noise Health. 2009;11(44):145-50. in the frequencies of 3, 4 or 6kHz, particularly in the first 10 to 15 years of exposure and, as the lesion worsens, it afterwards expands to frequencies 8, 2, 1, 0.5 and 0.25 kHz, which goes against the findings of this research, since Group 1 was exposed to higher levels of sound pressure and underwent longer exposure time (average of 20 years), and presented higher thresholds, albeit within the criteria of normality.
A range of studies has revealed hearing loss in the high frequencies, especially
with its beginning at 4kHz, with evolution for the circumjacent 6kHz and 3kHz
frequencies which, due to its being located in the basal region of the cochlea,
is firstly reached by the noise exposure, whether by the differences in the
mechanics of the cochlea, whether in the cochlear metabolism or in the cochlear
blood supply11 . Fernandes M, Morata TC. Estudo dos efeitos auditivos e
extra-auditivos da exposição ocupacional a ruído e vibração. Rev Bras
Otorrinolaringol. [periódico na internet]. 2002 Oct [cited 2011 Dec
22];68(5):705-13. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992002000500017&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992002000500017.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
,1212 . Job A, Raynal M, Kossowski M, Studler M, Ghernaouti C,
Baffioni-Venturi A et al. Otoacoustic detection of risk of early hearing loss in
ears with normal audiograms: a 3-year follow-up study. Hear Res.
2009;251(1-2):10-6.,1616 . Almeida SIC, Albernaz PLM, Zaia PA, Xavier OG, Karazawa EHI.
História natural da perda auditiva ocupacional provocada por ruído. Rev. Assoc.
Med. Bras. [periódico na internet]. 2000 [cited 2012-05-08];46(2):143-58.
Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-42302000000200009&lng=en&nrm=iso.
ISSN 0104-4230.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0104-42302000000200009.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
,1717 . Dias A, Cordeiro A, Corrente JE, Gonçalves CGO. Associação entre
perda auditiva induzida pelo ruído e zumbidos. Cad. Saúde Pública [periódico na
internet]. 2006 [cited 2011 Dec 22];22(1):63-8. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102-311X2006000100007&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2006000100007.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
,2020 . Lacerda A, Figueiredo G, Massarolo NJ, Marques JM. Achados
audiológicos e queixas relacionadas à audição dos motoristas de ônibus urbano.
Rev. soc. bras. Fonoaudiol. 2010;15(2):161-6.,2121 . Guida HL. Efeitos psicossociais da perda auditiva induzida pelo
ruído em ex-funcionários da indústria. ACTA ORL/Técnicas em
Otorrinolaringologia. 2006;25(1):78-83.. In this study, albeit the
hearing loss having not been identified in any of the tested frequencies, the
worst thresholds occurred in the 4kHz and 6kHz frequencies.
The quantitative analysis of the otoacoustic emission test evoked by transient stimuli showed a statistical difference, with predominance of absence of responses in both groups; however, the individuals of Group 1 had greater occurrence of TEOAE absence when compared to Group 2 (Chart 1). In Figure 2, it is easy to notice that there was significant statistic difference when the frequency bands tested in the TEOAE were analyzed, with greater relationship of signal/ noise in the frequency bands 1, 2 and 3 kHz in Group 2, in comparison with Group1. In addition, the General Response showed a tendency to significance, with greater amplitude of responses in Group 2, as well.
These results were similar to the ones found in other studies 2222 . Xu ZM., Van Cauwenberge P, Vinck B, De Vel E. (1998) Sensitive
detection of noise-induced damage in human subjects using transiently evoked
otoacoustic emissions. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg.
1998;52(1):19-24.,2323 . Sliwinska-Kowalska M, Kotylo P, Hendler B. Comparing changes in
transient-evoked otoacoustic emission and pure-tone audiometry following short
exposure to industrial noise. Noise Health. 1999;1(2):50-7., which registered an
expressive reduction in the amplitude, reproducibility and signal/ noise
relationship in the 1 a 4 kHz frequency bands in the TEOAE or even the absence
of emissions between individuals submitted to exposure and the control group.
Both groups showed DPOAE presence in all the tested frequencies, with the
exception of the 6kHz (Figure 3). Such test has also allowed the evaluation of
frequencies 5 and 6kHz, realizing statistically significant difference for 5kHz
frequency, with better responses in Group 2. It was noteworthy that the group
under higher level of noise exposure (Group 1) registered lower responses in all
the frequencies analyzed in the DPOAE. As for the 6kHz, it was the only
frequency that showed an amplitude average construed as altered in both groups.
Such findings match those of the studies that had recorded that the individuals
subjected to noise, even within the thresholds of the normality standard,
displayed lesser amplitude in the DPOAEor even the absence of one or more tested
frequencies, when compared with the control group1010 . Balatsouras DG. The evaluation of noise-induced hearing loss with
distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Med Sci Monit. [periódico na
internet]. 2004 May [citado 2011 Dez 22];10(5):CR218-22. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?ICID=11654.
http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?I...
,1111 . Marques FP, Costa EA. Exposição ao ruído ocupacional: alterações
no exame de emissões otoacústicas. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico na
internet]. 2006 [cited 2011 Dec 22];72(3):362-6. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992006000300011&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992006000300011.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
.
The fact that the current research refrains to portray the statistically significant difference when comparing the performance of both groups in the 4kHz frequency in the TEOAE test and in the 6kHz frequency in the DPOAE test, can be justified by the absence of a control group, that is, in this research, both the groups were exposed to noise, in lower or higher levels, that is, both revealed risk factor for hearing loss.
Besides, in other studies, the TEOAE and the DPOAE tests proved being more
sensitive regarding the identification of cochlear alteration than the tonal
liminal audiometry, having the TEOAE revealed greater sensitivity to cochlear
changes 55 . Otenio MH, Cremer E, Claro EMT. Intensidade de ruído em hospital
de 222 leitos na 18ª Regional de Saúde - PR. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico
na internet] 2007 Apr [cited 2011 Dec 22];73(2):245-50. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992007000200016&lng=en.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992007000200016.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
and the DPOAE allowed
the diagnosis of eventual lesion in higher levels, even in individuals with
quantitatively normal hearing regarding the tonal audiometry1010 . Balatsouras DG. The evaluation of noise-induced hearing loss with
distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Med Sci Monit. [periódico na
internet]. 2004 May [citado 2011 Dez 22];10(5):CR218-22. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?ICID=11654.
http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?I...
,1212 . Job A, Raynal M, Kossowski M, Studler M, Ghernaouti C,
Baffioni-Venturi A et al. Otoacoustic detection of risk of early hearing loss in
ears with normal audiograms: a 3-year follow-up study. Hear Res.
2009;251(1-2):10-6.,1313 . Coelho MSB, Ferraz JRS, Almeida EOC, Almeida FN. As emissões
otoacústicas no diagnóstico diferencial das perdas auditivas induzidas por
ruído. Rev. CEFAC [periódico na internet]. 2010 [cited 2011 Dec
22];12(6):1050-8. Disponível em: URL:
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-18462010000600017&lng=en.
Epub Nov 19, 2010.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-18462010005000108.
http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=s...
,2323 . Sliwinska-Kowalska M, Kotylo P, Hendler B. Comparing changes in
transient-evoked otoacoustic emission and pure-tone audiometry following short
exposure to industrial noise. Noise Health. 1999;1(2):50-7..
CONCLUSION
The levels of sound pressure and the exposure time have not played any influence for obtaining tonal hearing thresholds, since both groups disclosed hearing thresholds within the normality standards. Notwithstanding, the higher the level of sound and the longer the exposure period, more altered were the otoacoustic emissions. There is a preponderance of absence of responses in the otoacoustic emissions through transient stimuli in both groups, but Group 1 revealed greater occurrence of TEOAE absence. The 4kHz frequency band is equally compromised in the groups. The DPOAE appear in all the tested frequencies, with the exception of the 6kHz frequency, in both groups.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We thank the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) for their support for this research under process number 2010/05192-7.
REFERÊNCIAS
-
1Fernandes M, Morata TC. Estudo dos efeitos auditivos e extra-auditivos da exposição ocupacional a ruído e vibração. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol. [periódico na internet]. 2002 Oct [cited 2011 Dec 22];68(5):705-13. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992002000500017&lng=en. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992002000500017.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992002000500017&lng=en -
2Pereira RP, Toledo RN, Amaral JLG, Guilherme A. Qualificação e quantificação da exposição sonora ambiental em uma unidade de terapia intensiva geral. Rev. Bras. Otorrinolaringol. [periódico na internet] 2003 [citado 2011 Dez 22];69(6):766-71. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992003000600007&lng=pt. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992003000600007.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992003000600007&lng=pt -
3Rodarte MDO, Scochi CGS, Leite AM, Fujinaga CI, Zamberlan NE, Castral TC. O ruído gerado durante a manipulação das incubadoras: implicações para o cuidado de enfermagem. Rev. Latino-Am. Enfermagem. 2005;13(1):79-85.
-
4Achutan C. Assessment of noise exposure in a hospital kitchen. Noise Health. 2009;11(44):145-50.
-
5Otenio MH, Cremer E, Claro EMT. Intensidade de ruído em hospital de 222 leitos na 18ª Regional de Saúde - PR. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico na internet] 2007 Apr [cited 2011 Dec 22];73(2):245-50. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992007000200016&lng=en. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992007000200016.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992007000200016&lng=en -
6Macedo ISC, Mateus DC, Costa EMGC, Asprino ACL, Lourenço EA. Avaliação do ruído em Unidades de Terapia Intensiva. Braz. J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico na internet]. 2009 [cited 2011 Dec 22]; 75(6):844-6. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1808-86942009000600012&lng=en. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1808-86942009000600012.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1808-86942009000600012&lng=en -
7Silva MC, Orlandi CG, Chang EM, Siviero J, Pinto MM, Armellini PFS et al . Níveis de ruído na lavanderia de um hospital público. Rev. CEFAC. 2011;13(3):472-8.
-
8Silva MC. Níveis de ruído no ambiente hospitalar: impacto na qualidade de vida [dissertação]. São Paulo (SP): Universidade Federal de São Paulo; 2009.
-
9Leme OLS. Estudo audiométrico comparativo entre trabalhadores de área hospitalar expostos e não expostos a ruído. Rev. Bras. Otorrinolaringol [periódico na internet]. 2001 [citado 2011 Dez 22];67(6):837-43. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992001000600013&lng=pt. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992001000600013.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992001000600013&lng=pt -
10Balatsouras DG. The evaluation of noise-induced hearing loss with distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Med Sci Monit. [periódico na internet]. 2004 May [citado 2011 Dez 22];10(5):CR218-22. Disponível em: URL: http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?ICID=11654.
» http://www.medscimonit.com/fulltxt.php?ICID=11654 -
11Marques FP, Costa EA. Exposição ao ruído ocupacional: alterações no exame de emissões otoacústicas. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. [periódico na internet]. 2006 [cited 2011 Dec 22];72(3):362-6. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992006000300011&lng=en. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-72992006000300011.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992006000300011&lng=en -
12Job A, Raynal M, Kossowski M, Studler M, Ghernaouti C, Baffioni-Venturi A et al. Otoacoustic detection of risk of early hearing loss in ears with normal audiograms: a 3-year follow-up study. Hear Res. 2009;251(1-2):10-6.
-
13Coelho MSB, Ferraz JRS, Almeida EOC, Almeida FN. As emissões otoacústicas no diagnóstico diferencial das perdas auditivas induzidas por ruído. Rev. CEFAC [periódico na internet]. 2010 [cited 2011 Dec 22];12(6):1050-8. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-18462010000600017&lng=en. Epub Nov 19, 2010. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-18462010005000108.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-18462010000600017&lng=en -
14Ogido R, Costa EA, Machado HC. Prevalência de sintomas auditivos e vestibulares em trabalhadores expostos a ruído ocupacional. Rev. Saúde Pública [periódico na internet]. 2009 [cited 2011 Dec 22];43(2):377-80. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-89102009000200021&lng=en. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0034-89102009000200021.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-89102009000200021&lng=en -
15Durante AS. Emissões Otoacústicas. In: Bevilacqua MC, Martinez MAN, Balen AS, Pupo AC, Reis ACM, Frota S. Tratado de Audiologia. São Paulo: Santos; 2011. p. 145-58.
-
16Almeida SIC, Albernaz PLM, Zaia PA, Xavier OG, Karazawa EHI. História natural da perda auditiva ocupacional provocada por ruído. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. [periódico na internet]. 2000 [cited 2012-05-08];46(2):143-58. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-42302000000200009&lng=en&nrm=iso. ISSN 0104-4230. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0104-42302000000200009.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-42302000000200009&lng=en&nrm=iso -
17Dias A, Cordeiro A, Corrente JE, Gonçalves CGO. Associação entre perda auditiva induzida pelo ruído e zumbidos. Cad. Saúde Pública [periódico na internet]. 2006 [cited 2011 Dec 22];22(1):63-8. Disponível em: URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102-311X2006000100007&lng=en. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0102-311X2006000100007.
» http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0102-311X2006000100007&lng=en -
18World Health Organization. Occupational and community noise. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001.
-
19Comitê Nacional de Ruído e Conservação Auditiva. Perda auditiva induzida por ruído relacionada ao trabalho. Boletim, São Paulo, n. 1, 29 jun. 1994. Revisto em 14 nov. 1999.
-
20Lacerda A, Figueiredo G, Massarolo NJ, Marques JM. Achados audiológicos e queixas relacionadas à audição dos motoristas de ônibus urbano. Rev. soc. bras. Fonoaudiol. 2010;15(2):161-6.
-
21Guida HL. Efeitos psicossociais da perda auditiva induzida pelo ruído em ex-funcionários da indústria. ACTA ORL/Técnicas em Otorrinolaringologia. 2006;25(1):78-83.
-
22Xu ZM., Van Cauwenberge P, Vinck B, De Vel E. (1998) Sensitive detection of noise-induced damage in human subjects using transiently evoked otoacoustic emissions. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 1998;52(1):19-24.
-
23Sliwinska-Kowalska M, Kotylo P, Hendler B. Comparing changes in transient-evoked otoacoustic emission and pure-tone audiometry following short exposure to industrial noise. Noise Health. 1999;1(2):50-7.
-
Source of support: Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
Publication Dates
-
Publication in this collection
may-jun 2014
History
-
Received
02 Jan 2013 -
Accepted
15 May 2013