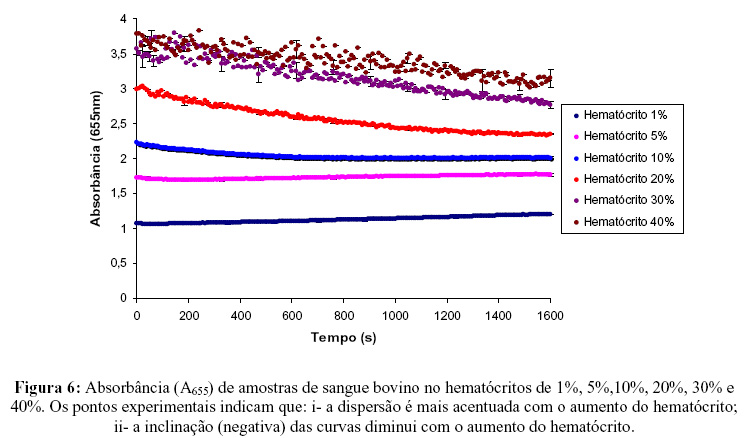
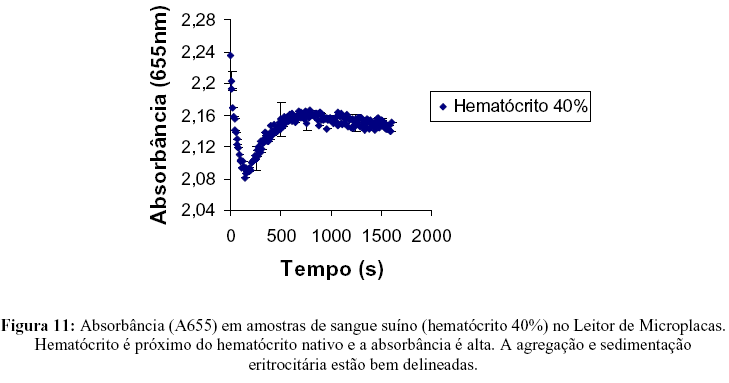
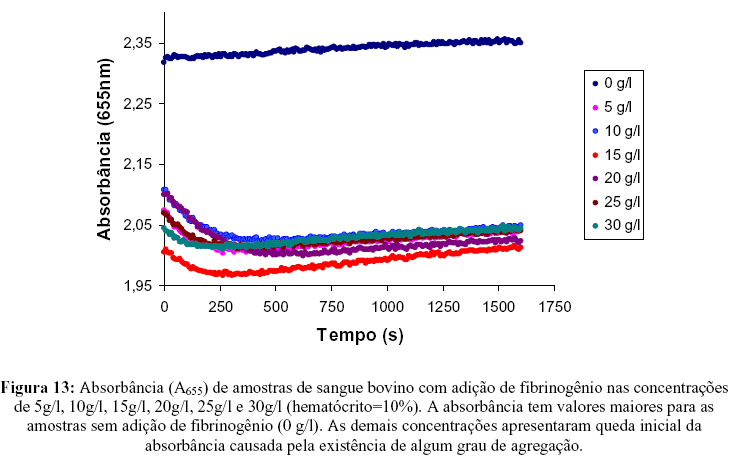
The presence of some macromolecules in the blood is associated with blood hiperviscosity and hyperaggregation. We have studied erythrocyte aggregation and blood sedimentation on samples of swine, human and bovine blood. Bovine blood does not present erythrocyte aggregation while human and swine blood naturally aggregates at low shear rates and at stasis. The action of different bovine fibrinogen concentrations on the microstructure of bovine blood was analyzed and compared with swine and human blood. The phenomena were investigated using optical microscopy (to analyze blood microstructures) and Microplate Reader to measure absorbance (at a fixed wavelength, l=655nm) versus time(s). Experiments were performed using samples of bovine blood (hematocrit 40%), swine blood (H= 1%, 5%, 10%, 30% and 40%) and human blood (H= 40%); and samples of bovine blood (H= 40%) with the addition of bovine fibrinogen at different concentrations (5g/l, 10g/l, 20g/l, 25g/l and 30g/l). Using the Microplate Reader it was possible to distinguish three regions in the process: a-The region I where the erythrocyte aggregation occurs; b-region II where the sedimentation process is predominant and c-Region III where a very slow increase indicates that the persistence of sedimentation process. The association of the optical microscopy with the Microplate Reader technique makes possible the determination of quantitative parameters for the process of aggregation and sedimentation. These parameters will facilitate the diagnosis and a more accurate analysis of the evolution of pathologies that afflict both humans as animals.
Erythrocyte aggregation; fibrinogen; aggregation