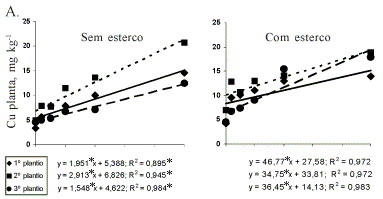
A greenhouse experiment was conducted to evaluate the effects of varying doses of Cu (0 to 5.0 mmol kg-1 ) and Zn (0 to 2.0 mmol kg-1) added to a Cambisol on the dry matter and mineral composition of snap beans. Separately the metals were added to the soil and after 30 days plant dry matter and Cu and Zn contents in aerial part and in the roots. The metal contents in the plant tissues were correlated with those present in the soil extracted with 1.0 mol L-1 NH4OAc pH 4.8 and 7.0, and 5.0 mmol L-1 DTPA pH 6.8. The Cu content in aerial part and roots increased in proportion to the doses added to soil. The accumulation of Cu in the roots was ten times greater than that found in the aerial part and increased with the Cu rates in soil up to 5.0 mmol kg-1. At application rate of 5.0 mmol kg-1 of soil, beans did not show phytotoxicity symptoms and the Cu concentration in the aerial part was below the normal level. The DTPA solution showed the best correlation of soil-Cu with aerial part-Cu and root-Cu. The contents of Zn in the bean root tissues increased with increasing contents of metal in soil. The Zn concentration in the roots (330 mg kg-1) was greater than found in the aerial part (310 mg kg-1). But did not show toxicity symptoms in the leaves even in the highest Zn rates and did not reduce the dry matter production. The three soil-Zn extraction solutions showed high correlation with Zn concentration in the aerial part and in the roots of beans.
Phaseolus vulgaris; heavy metal; soil polution