ABSTRACT
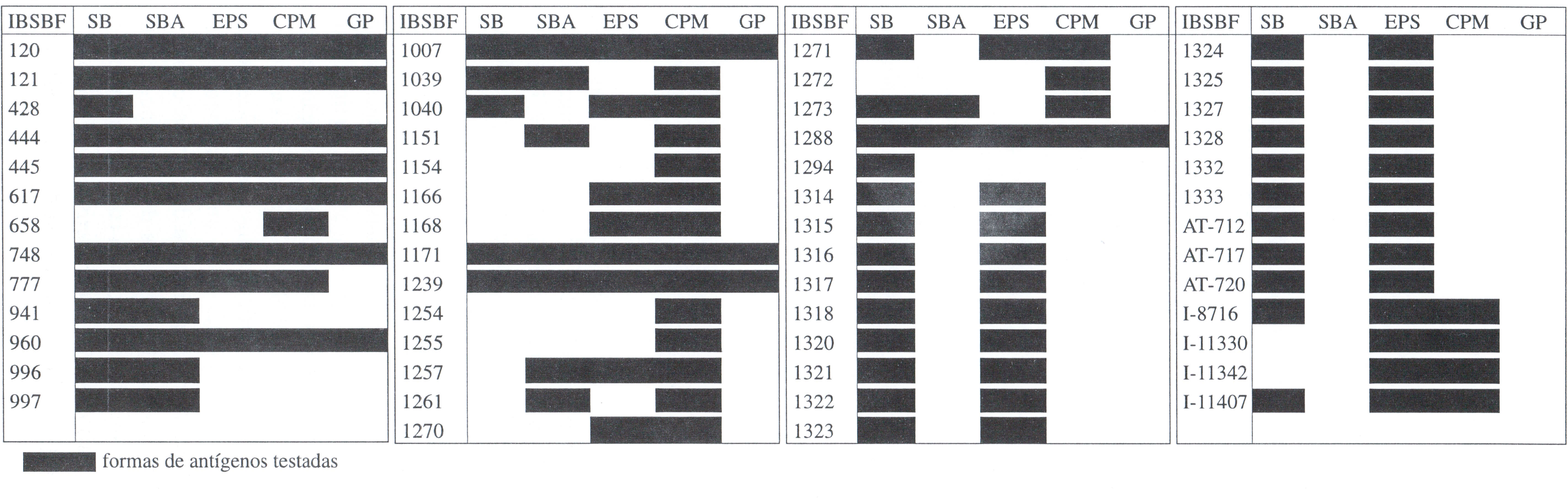
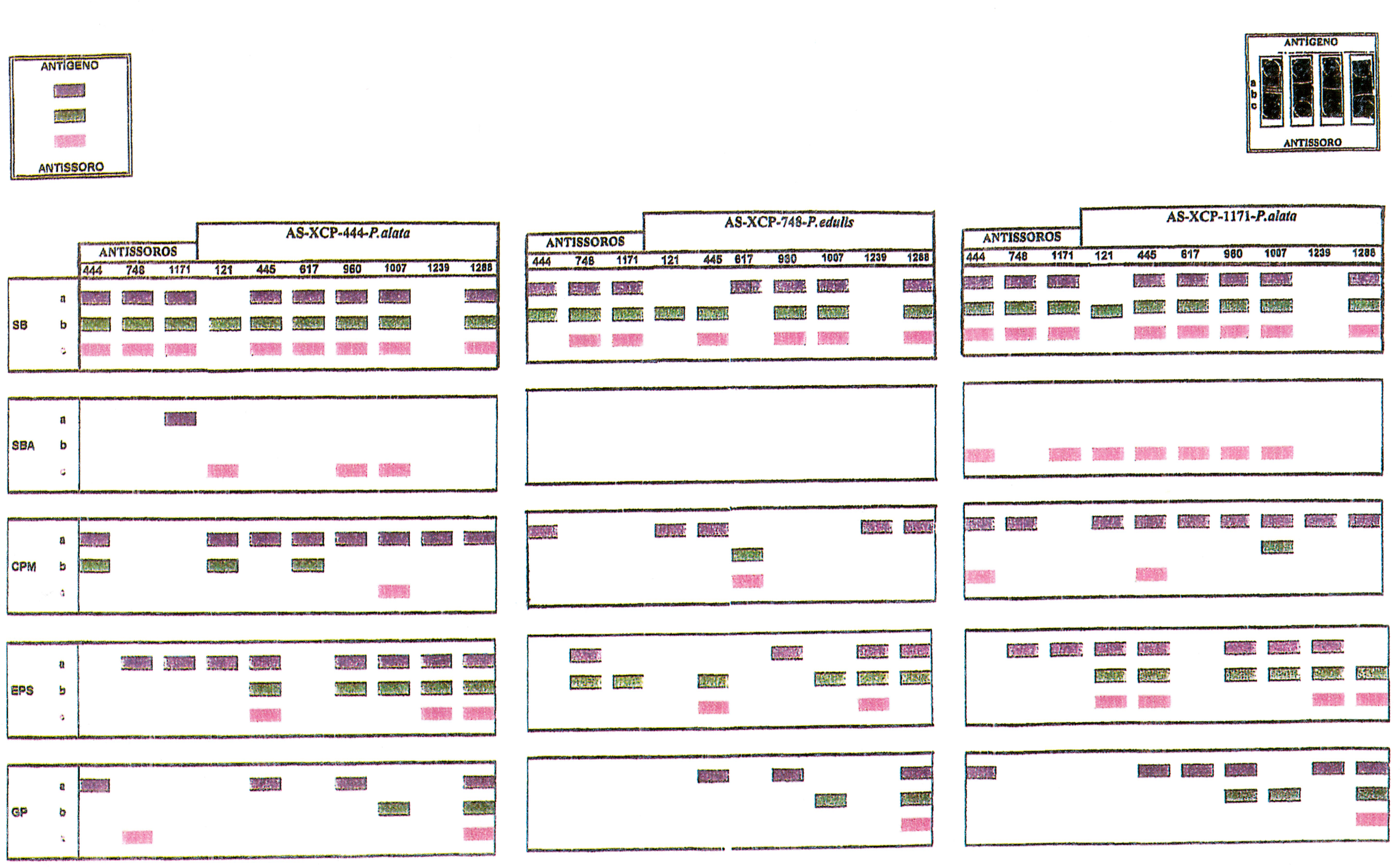
The bacterial disease of passion fruit (Passiflora spp), caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. passiflorae, is the most important disease in this crop in Brazil and can be a commercial restriction for its commercial cultivation. Fifty-four strains of X. e. pv. passiflorae were analysed by serology, through double diffusion agar test (d.d.a.). Antisera were produced against two strains of X e. pv. passiflorae from P. alata (AS-XCP-444 and AS-XCP-1171) and one strain from P. edulis ( AS-XCP-748). Antigens were prepared as bacterial suspension (BS), autoclaved bacterial suspension (ABS), extracellular polysacharides (EPS), membrane protein complex (MPC) and glycoprotein (GP). All antigens were tested with the three antisera. The results showed that the BS and MPC antigens were the most efficient for pv. passiflorae diagnosis, using material under suspected infection. Although the ABS, EPS and GP antigens could not be employed for X. e. pv. passiflorae diagnosis, if purified, they can be used in serogroups screening.
KEY WORDS:
Xanthomonas campestris pv passiflorae;
Passiflora edulis
; serology
 SEROLOGY APPLIED TO THE STUDY OF XANTHOMONAS CAMPESTRIS PV. PASSIFLORAE, A CAUSITIVE AGENT 1N BACTERIOSIS OF THE PASSION FRUIT TREE (PASSIFLORA SPP)
SEROLOGY APPLIED TO THE STUDY OF XANTHOMONAS CAMPESTRIS PV. PASSIFLORAE, A CAUSITIVE AGENT 1N BACTERIOSIS OF THE PASSION FRUIT TREE (PASSIFLORA SPP) Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail