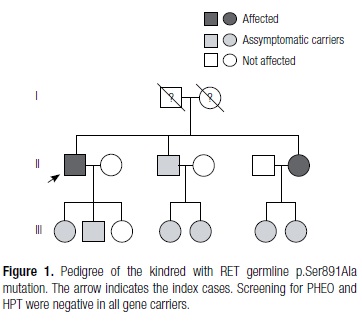
Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is a malignant tumor originating from parafollicular C-cells and accounts for 4-10% of all thyroid carcinomas. MTC develops in either sporadic (75%) or hereditary form (25%). Mutations in the RET proto-oncogene are responsible for hereditary MTC and the rate of heritable disease among apparently sporadic MTC (sMTC) cases varies from 6 to 15%. RET genetic testing is now considered fundamental in MTC management but the extent of the molecular analysis required to exclude inherited disease is still controversial. While the screening of all known mutation loci is recommended by some authors, the high costs associated with a full analysis should be also taken into consideration. Here, we illustrate and discuss this controversial issue by reporting a patient who present all characteristic features of sMTC, and in whom a standard genetic analysis by restriction enzyme restriction excluded hereditary disease. Nevertheless, an extensive molecular analysis that included all codons was prompted by the diagnosis of thyroid neoplasm in a patient's sister, and identified the rare intracellular RET p.Ser891Ala mutation. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2012;56(8):586-91