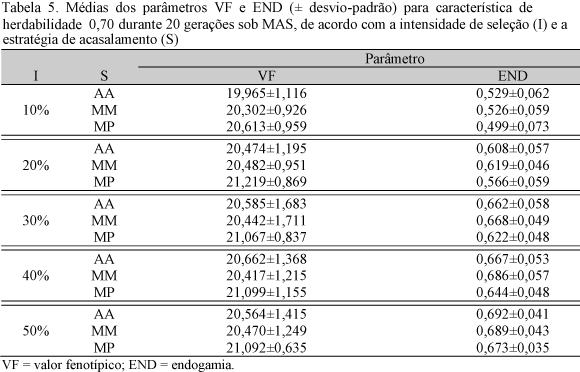
Different strategies of selection were simulated to estimate the phenotypic performance and average inbreeding in selection assisted by markers, for quantitative traits with heritability values of 0.10, 0.40, and 0.70. The genetic simulation system (Genesys) was used for the simulation of three genomes (each one consisting of a single characteristic which distinction was the value of heritability) and base and original populations. Each initial population was subjected to selection assisted by markers for 20 consecutive generations. Strategies of mating between the parents selected in different intensities of selection (population size) were evaluated by selective mating between the best and worst, mating only among the best and/or among the worst and random mating. In all scenarios combining heritability and intensity, the strategic mating using the methodology of selective genotyping was superior to the others, becoming more effective in detecting QTL and, consequently, in the increase of phenotypic value and in the minimization of the inbred average over the generations. By using the selective sampling strategy, smaller population size to optimize the detection of QTL is required, since the value of the heritability of the characteristic increases.
heritability; strategic selection; simulation; QTL