Abstract
The great heterogeneity of construction and demolition waste (CDW) hinders its systematic use, leading to problems in its final disposal and in the continual extraction and use of non-renewable resources in concrete manufacturing. This heterogeneity derives primarily from the fact that manufacturers do not segregate the wide variety of CDW components during their processing. This paper analyses the need to segregate CDW into two different types - clay ceramics (red) and rocks and cement (gray) - and the consequences of using these materials as substitutes for natural coarse aggregates in structural concrete. Hence, different concretes were manufactured with 25, 50 and 100% CDW, using three types of waste: cementitious, ceramic and a mixture of both. The conclusion is that it is not necessary to segregate the waste from the recycling plant, since the results show that the concrete with cementitious aggregates and the one with mixed aggregates perform similarly. In addition, the use of CDW affects the characteristics of the concrete. Rheological and mechanical performance are parameters negatively affected by the use of waste. However, durability may improve with the use of recycled aggregates.
Keywords:
Construction and demolition waste; Concrete; Durability; Mechanical characterization

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
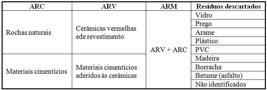
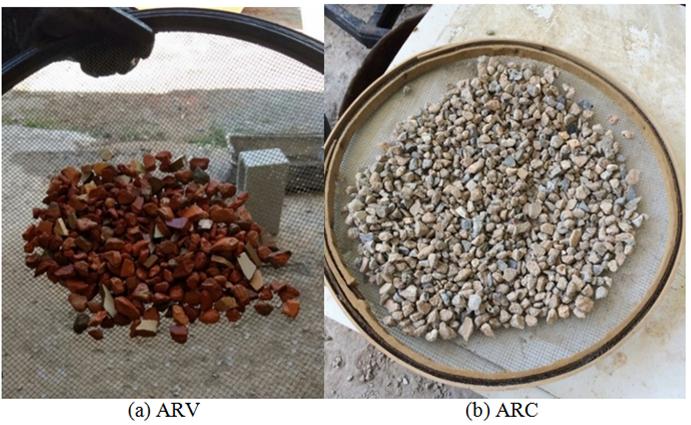
 Nota: Legenda: ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e PVC: policloreto de vinila.
Nota: Legenda: ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e PVC: policloreto de vinila.

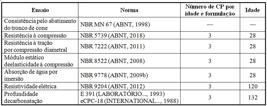
 Fonte: ABNT (
Fonte: ABNT ( Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
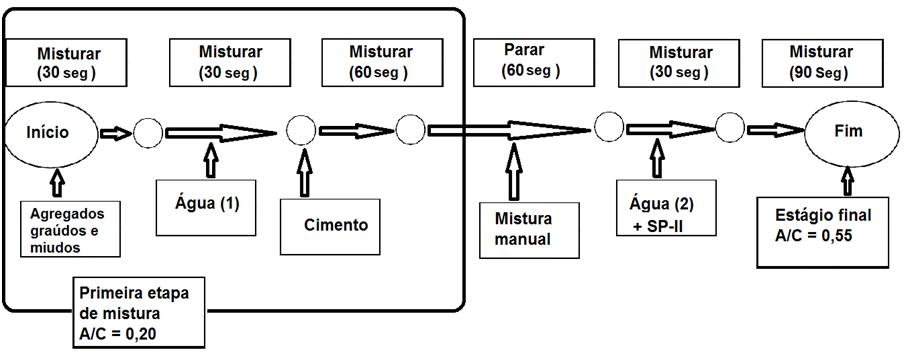 Fonte: adaptado de
Fonte: adaptado de 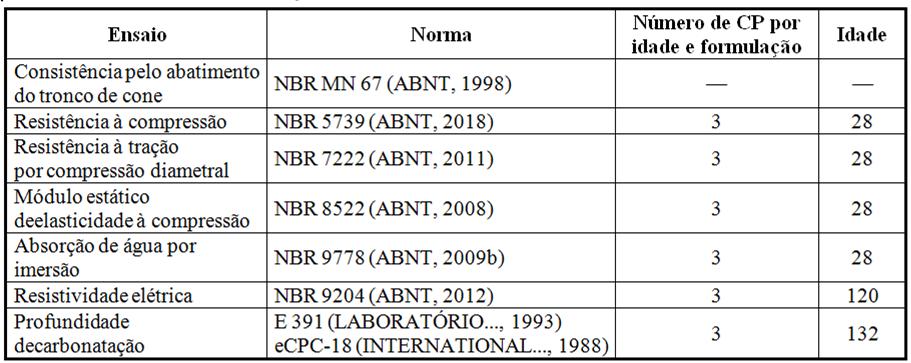 Fonte: ABNT (
Fonte: ABNT (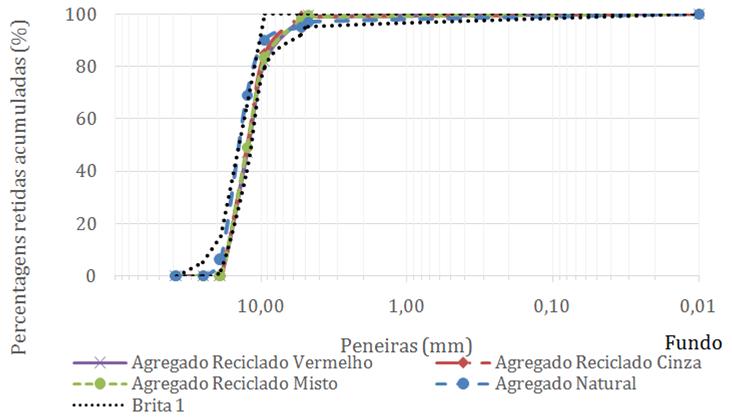
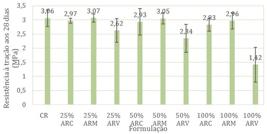
 Nota: Legenda: ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; e ARM: agregado reciclado misto.
Nota: Legenda: ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; e ARM: agregado reciclado misto.
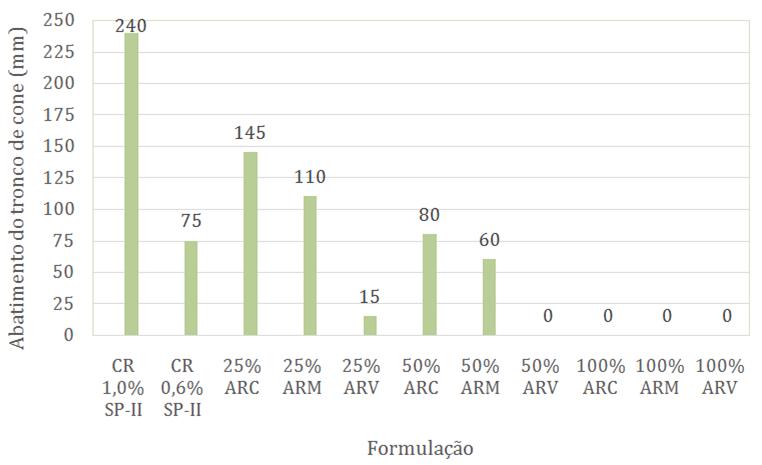 Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; SP-II: superplastificante tipo II; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; SP-II: superplastificante tipo II; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
 Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
 Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
 Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
 Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
 Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
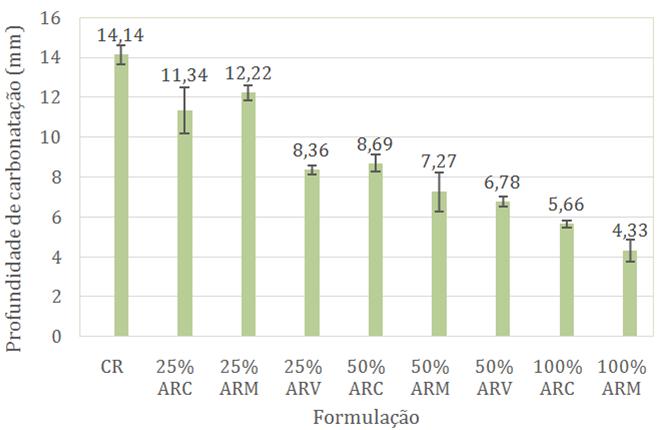 Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.
Nota: Legenda: CR: concreto de referência; ARC: agregado reciclado cinza; ARM: agregado reciclado misto; e ARV: agregado reciclado vermelho.