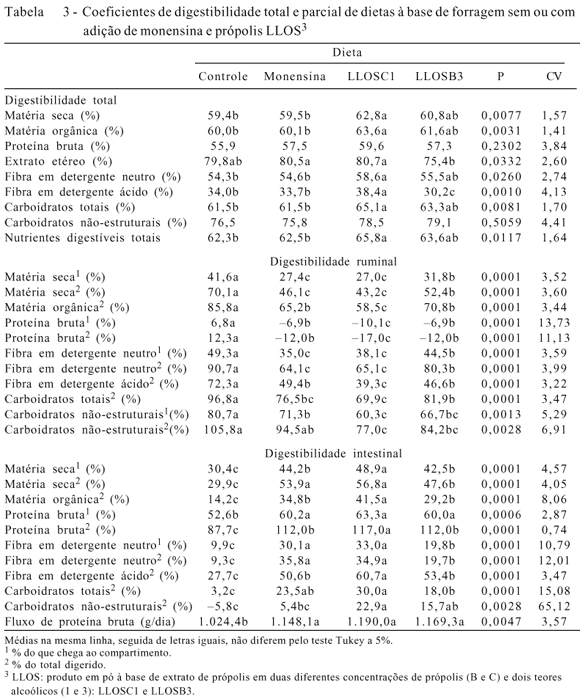
The objective of this work was to study the effect of the administration of products based on sodium monesin or propolis LLOSB3 and LLOSC1 in two concentrations (B and C, in which B was less concentrated than C) and two alcoholic extractions (1 and 3, in which 1 was less concentrated than 3) on intake, total and partial digestibility, and ruminal characteristics in buffaloes fed diet based on roughage. It was used four castrated crossbred buffalo with average weight of 459.3 ± 44.5 kg in 4 x 4 experimental Latin square design with four diets (control, monensin, LLOSC1 and LLOSB3) and four periods. The diet had 80% roughage (corn silage and Tifton hay) and 20% concentrate, with 11.1% CP and 66% of total digestible nutrients (TDN). The intake of dry matter (DM) and nutrients did not differ among tested additives. The addition of LLOSC1 provided higher total digestibility coefficients in relation to the control for dry matter (62.8% vs. 59.4%), NDF (58.6% vs. 54.3%), total carbohydrates (65.1% vs. 61.5%) and TDN (65.8 vs. 62.3%). The diet with monensin did not differ from the control and the diet with LLOSB3 was similar to all other diets. Increase in the flow and higher digestibility of CP in the intestines were found with the use of additives in relation to the control diet. After feeding at 2.18 h, there was no difference in the concentration of ammoniacal nitrogen in the rumen among diets and the maximum value was 21.26 mg/100 mL. The lowest value of ruminal pH (6.48) and higher concentrations of acetate and butyrate were found for LLOSB3. The passage rate of liquid did not differ among diets, however greater ruminal volume was found with the use of additives. The additive LLOSC1 is superior than monensin in increasing digestible energy for buffalo fed diets based on roughage.
additives; ammonia nitrogen; intake; partial digestibility; volatile fatty acids